Mechanisms Linking the Gut Microbiome and Glucose Metabolism
- PMID: 26938201
- PMCID: PMC4880177
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2015-4251
Mechanisms Linking the Gut Microbiome and Glucose Metabolism
Erratum in
-
ERRATUM.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Jun;101(6):2622. doi: 10.1210/jc.2016-2006. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 28059606 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
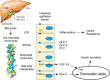
This review details potential mechanisms linking gut dysbiosis to metabolic dysfunction, including lipopolysaccharide, bile acids, short chain fatty acids, gut hormones, and branched-chain amino acids.
Figures

References
-
- Hayashi H, Takahashi R, Nishi T, Sakamoto M, Benno Y. Molecular analysis of jejunal, ileal, caecal and recto-sigmoidal human colonic microbiota using 16S rRNA gene libraries and terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism. J Med Microbiol. 2005;54:1093–1101. - PubMed
-
- Tremaroli V, Backhed F. Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature. 2012;489:242–249. - PubMed
-
- Hullar MA, Lampe JW. The gut microbiome and obesity. Nestle Nutr Instit Workshop Series. 2012;73:67–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

