Defects in the NC2 repressor affect both canonical and non-coding RNA polymerase II transcription initiation in yeast
- PMID: 26939779
- PMCID: PMC4778323
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-016-2536-2
Defects in the NC2 repressor affect both canonical and non-coding RNA polymerase II transcription initiation in yeast
Abstract
Background: The formation of the pre-initiation complex in eukaryotic genes is a key step in transcription initiation. The TATA-binding protein (TBP) is a universal component of all pre-initiation complexes for all kinds of RNA polymerase II (RNA pol II) genes, including those with a TATA or a TATA-like element, both those that encode proteins and those that transcribe non-coding RNAs. Mot1 and the negative cofactor 2 (NC2) complex are regulators of TBP, and it has been shown that depletion of these factors in yeast leads to defects in the control of transcription initiation that alter cryptic transcription levels in selected yeast loci.
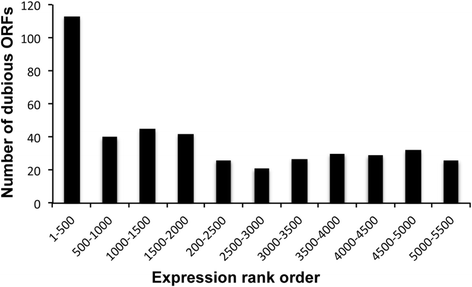
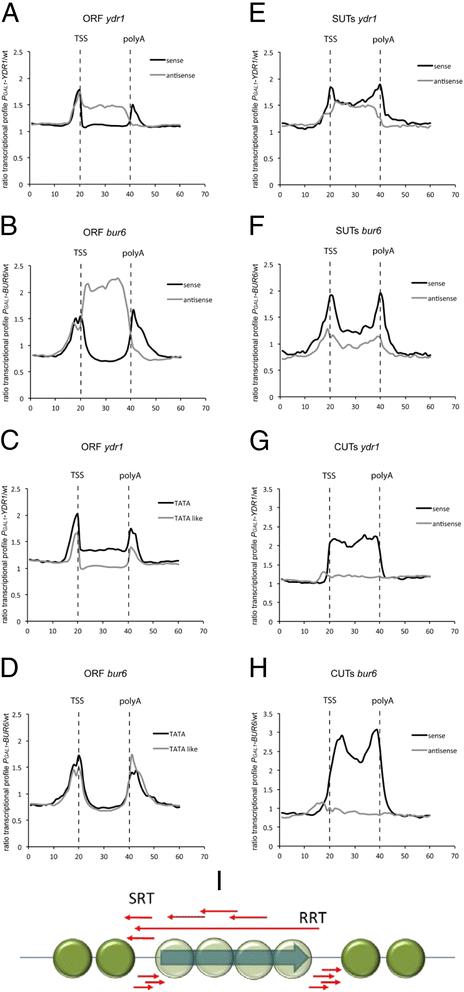
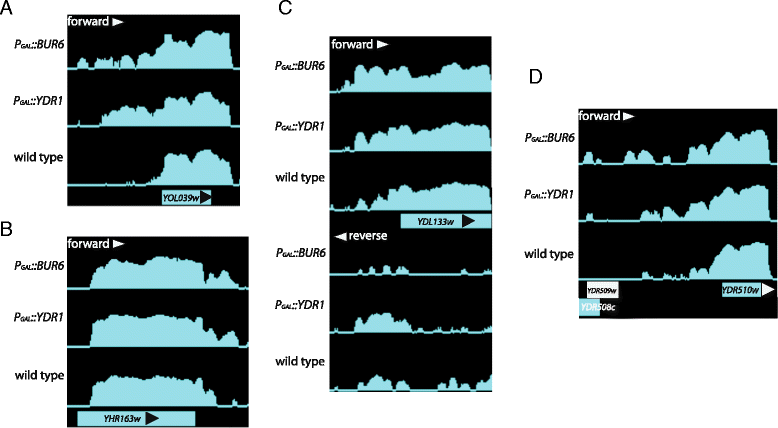
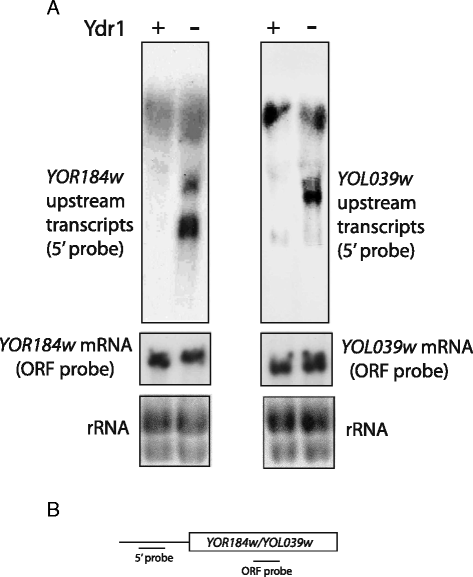
Results: In order to cast light on the molecular functions of NC2, we performed genome-wide studies in conditional mutants in yeast NC2 essential subunits Ydr1 and Bur6. Our analyses show a generally increased level of cryptic transcription in all kinds of genes upon depletion of NC2 subunits, and that each kind of gene (canonical or ncRNAs, TATA or TATA-like) shows some differences in the cryptic transcription pattern for each NC2 mutant.
Conclusions: We conclude that NC2 plays a general role in transcription initiation in RNA polymerase II genes that is related with its known TBP interchange function from free to promoter bound states. Therefore, loss of the NC2 function provokes increases in cryptic transcription throughout the yeast genome. Our results also suggest functional differences between NC2 subunits Ydr1 and Bur6.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mot1, Ino80C, and NC2 Function Coordinately to Regulate Pervasive Transcription in Yeast and Mammals.Mol Cell. 2017 Aug 17;67(4):594-607.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.06.029. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Mol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28735899 Free PMC article.
-
Mot1 associates with transcriptionally active promoters and inhibits association of NC2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Dec;22(23):8122-34. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.23.8122-8134.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12417716 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast NC2 associates with the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex and selectively affects transcription in vivo.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Apr;21(8):2736-42. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.8.2736-2742.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11283253 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and basal transcription complex of RNA polymerase II core promoters in the mammalian genome: an overview.Mol Biotechnol. 2010 Jul;45(3):241-7. doi: 10.1007/s12033-010-9265-6. Mol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20300884 Review.
-
SPT genes: key players in the regulation of transcription, chromatin structure and other cellular processes.J Biochem. 2001 Feb;129(2):185-91. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a002842. J Biochem. 2001. PMID: 11173517 Review.
Cited by
-
The negative cofactor 2 complex is a key regulator of drug resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus.Nat Commun. 2020 Jan 22;11(1):427. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-14191-1. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 31969561 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating quantitative proteomics with accurate genome profiling of transcription factors by greenCUT&RUN.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 May 21;49(9):e49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab038. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33524153 Free PMC article.
-
Aspergillus fumigatus Transcription Factors Involved in the Caspofungin Paradoxical Effect.mBio. 2020 Jun 16;11(3):e00816-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00816-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32546620 Free PMC article.
-
Mot1, Ino80C, and NC2 Function Coordinately to Regulate Pervasive Transcription in Yeast and Mammals.Mol Cell. 2017 Aug 17;67(4):594-607.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.06.029. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Mol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28735899 Free PMC article.
-
The lncRNA PDIA3P Interacts with miR-185-5p to Modulate Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression by Targeting Cyclin D2.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017 Dec 15;9:100-110. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2017.08.015. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017. PMID: 29246288 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

