De novo assembly and comparative transcriptome analysis of Euglena gracilis in response to anaerobic conditions
- PMID: 26939900
- PMCID: PMC4778363
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-016-2540-6
De novo assembly and comparative transcriptome analysis of Euglena gracilis in response to anaerobic conditions
Abstract
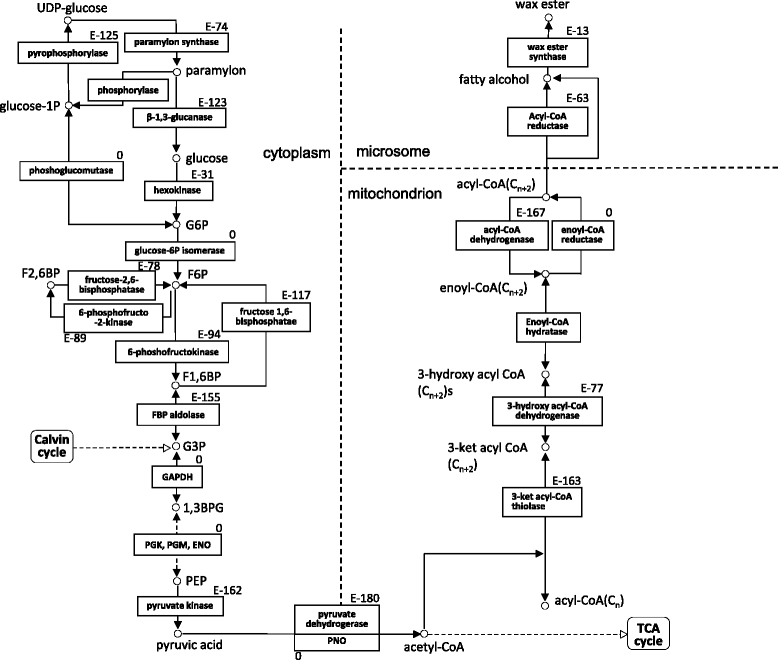
Background: The phytoflagellated protozoan, Euglena gracilis, has been proposed as an attractive feedstock for the accumulation of valuable compounds such as β-1,3-glucan, also known as paramylon, and wax esters. The production of wax esters proceeds under anaerobic conditions, designated as wax ester fermentation. In spite of the importance and usefulness of Euglena, the genome and transcriptome data are currently unavailable, though another research group has recently published E.gracilis transcriptome study during our submission. We herein performed an RNA-Seq analysis to provide a comprehensive sequence resource and some insights into the regulation of genes including wax ester metabolism by comparative transcriptome analysis of E.gracilis under aerobic and anaerobic conditions.
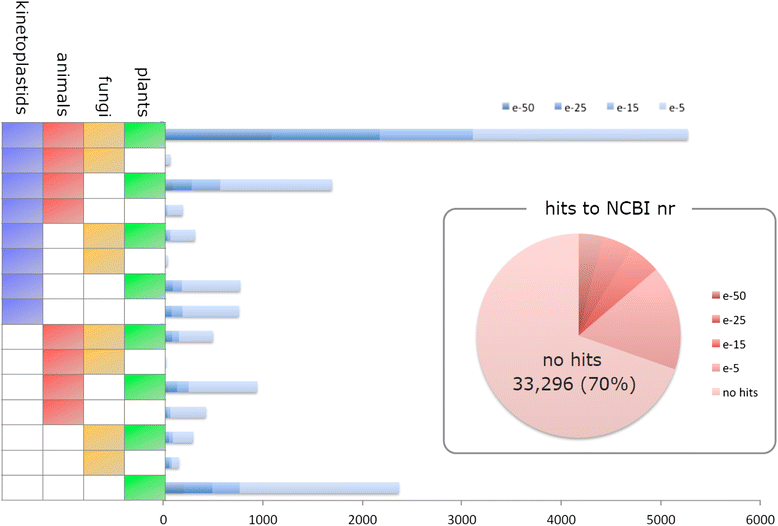
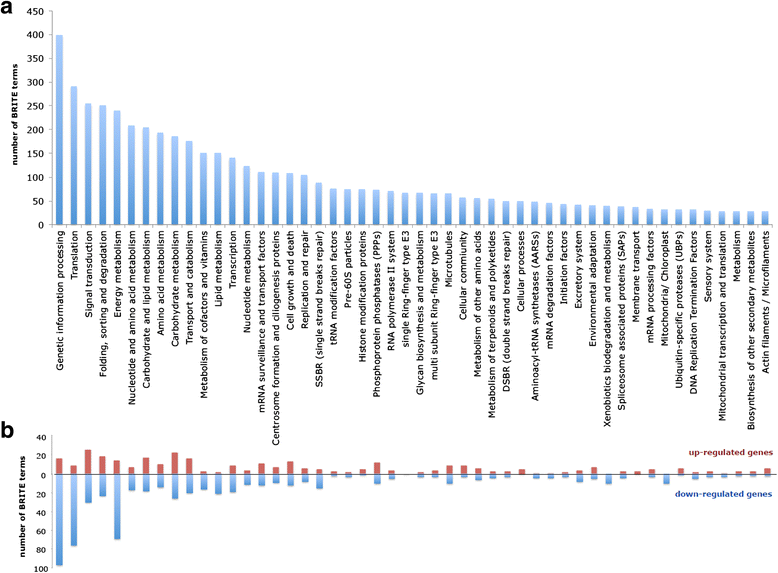
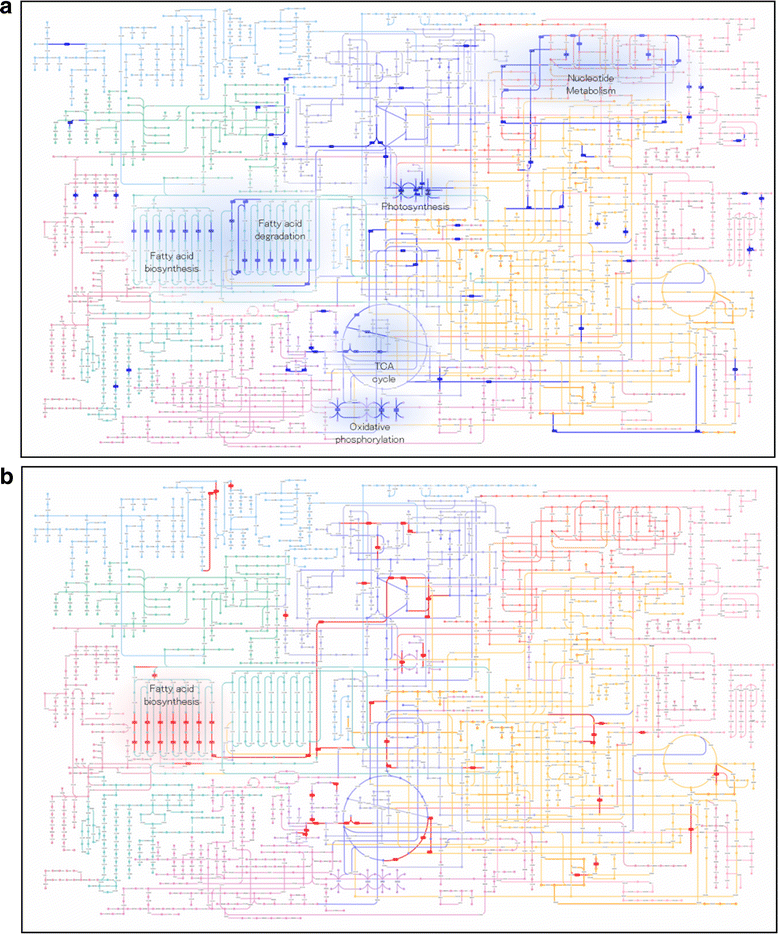
Results: The E.gracilis transcriptome analysis was performed using the Illumina platform and yielded 90.3 million reads after the filtering steps. A total of 49,826 components were assembled and identified as a reference sequence of E.gracilis, of which 26,479 sequences were considered to be potentially expressed (having FPKM value of greater than 1). Approximately half of all components were estimated to be regulated in a trans-splicing manner, with the addition of protruding spliced leader sequences. Nearly 40 % of 26,479 sequences were annotated by similarity to Swiss-Prot database using the BLASTX program. A total of 2080 transcripts were identified as differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in response to anaerobic treatment for 24 h. A comprehensive pathway enrichment analysis using the KEGG pathway revealed that the majority of DEGs were involved in photosynthesis, nucleotide metabolism, oxidative phosphorylation, fatty acid metabolism. We successfully identified a candidate gene set of paramylon and wax esters, including novel β-1,3-glucan and wax ester synthases. A comparative expression analysis of aerobic- and anaerobic-treated E.gracilis cells indicated that gene expression changes in these components were not extensive or dynamic during the anaerobic treatment.
Conclusion: The RNA-Seq analysis provided comprehensive transcriptome information on E.gracilis for the first time, and this information will advance our understanding of this unique organism. The comprehensive analysis indicated that paramylon and wax ester metabolic pathways are regulated at post-transcriptional rather than the transcriptional level in response to anaerobic conditions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Variability of wax ester fermentation in natural and bleached Euglena gracilis Strains in response to oxygen and the elongase inhibitor flufenacet.J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2010 Jan-Feb;57(1):63-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.2009.00452.x. Epub 2009 Dec 10. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20015184
-
Comparative profiling analysis of central metabolites in Euglena gracilis under various cultivation conditions.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2011;75(11):2253-6. doi: 10.1271/bbb.110482. Epub 2011 Nov 7. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 22056447
-
Wax Ester Fermentation and Its Application for Biofuel Production.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;979:269-283. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-54910-1_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28429326 Review.
-
Identification and characterization of cytosolic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase in Euglena gracilis.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2015;79(12):1957-64. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2015.1069694. Epub 2015 Jul 27. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26214137
-
Understanding wax ester synthesis in Euglena gracilis: Insights into mitochondrial anaerobic respiration.Protist. 2023 Dec;174(6):125996. doi: 10.1016/j.protis.2023.125996. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Protist. 2023. PMID: 38041972 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA-Seq employing a novel rRNA depletion strategy reveals a rich repertoire of snoRNAs in Euglena gracilis including box C/D and Ψ-guide RNAs targeting the modification of rRNA extremities.RNA Biol. 2018;15(10):1309-1318. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2018.1526561. Epub 2018 Oct 9. RNA Biol. 2018. PMID: 30252600 Free PMC article.
-
De Novo Assembly and Comparative Transcriptome Profiling of Anser anser and Anser cygnoides Geese Species' Embryonic Skin Feather Follicles.Genes (Basel). 2019 May 8;10(5):351. doi: 10.3390/genes10050351. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31072014 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of sulfur-compound metabolism underlying wax-ester fermentation in Euglena gracilis.Sci Rep. 2019 Jan 29;9(1):853. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36600-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30696857 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Euglena gracilis β-1,3-glucan phosphorylase and establishment of a new glycoside hydrolase (GH) family GH149.J Biol Chem. 2018 Feb 23;293(8):2865-2876. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000936. Epub 2018 Jan 9. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29317507 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of metabolic capabilities and molecular features of diplonemids, kinetoplastids, and euglenids.BMC Biol. 2020 Mar 2;18(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12915-020-0754-1. BMC Biol. 2020. PMID: 32122335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mata TM, Martins AA, Caetano NS. Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications: A review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2010;14:217–232. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2009.07.020. - DOI
-
- Barras DR, Stone BA. Carbohydrate composition and metabolism in Euglena. In: Edited by Buetow DE. The Biology of Euglena vol. 2. Academic Press, New York; 1968. 149–191.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

