Clonal neoantigens elicit T cell immunoreactivity and sensitivity to immune checkpoint blockade
- PMID: 26940869
- PMCID: PMC4984254
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aaf1490
Clonal neoantigens elicit T cell immunoreactivity and sensitivity to immune checkpoint blockade
Abstract
As tumors grow, they acquire mutations, some of which create neoantigens that influence the response of patients to immune checkpoint inhibitors. We explored the impact of neoantigen intratumor heterogeneity (ITH) on antitumor immunity. Through integrated analysis of ITH and neoantigen burden, we demonstrate a relationship between clonal neoantigen burden and overall survival in primary lung adenocarcinomas. CD8(+)tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes reactive to clonal neoantigens were identified in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer and expressed high levels of PD-1. Sensitivity to PD-1 and CTLA-4 blockade in patients with advanced NSCLC and melanoma was enhanced in tumors enriched for clonal neoantigens. T cells recognizing clonal neoantigens were detectable in patients with durable clinical benefit. Cytotoxic chemotherapy-induced subclonal neoantigens, contributing to an increased mutational load, were enriched in certain poor responders. These data suggest that neoantigen heterogeneity may influence immune surveillance and support therapeutic developments targeting clonal neoantigens.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures
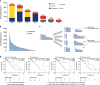

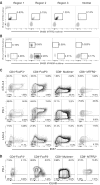
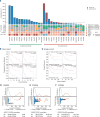
Comment in
-
Immunotherapy: Clonal neoantigens and immune response: a balancing act.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2016 May;13(5):265. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.49. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27030076 No abstract available.
-
Tumor Heterogeneity and Tumor Immunity: A Chicken-and-Egg Problem.Trends Immunol. 2016 Jun;37(6):349-351. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2016.04.008. Epub 2016 May 8. Trends Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27166403
References
-
- Castle JC, et al. Cancer Res. 2012;72:1081–1091. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1R01CA182461-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA205426/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 20466/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 17786/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 20265/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 12100/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01CA184922-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA182461/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 21999/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 1R01CA155010-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA184922/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA155010/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

