A Specialized Mechanism of Translation Mediated by FXR1a-Associated MicroRNP in Cellular Quiescence
- PMID: 26942679
- PMCID: PMC4811377
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.02.013
A Specialized Mechanism of Translation Mediated by FXR1a-Associated MicroRNP in Cellular Quiescence
Abstract
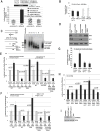
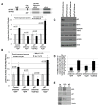
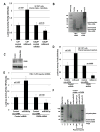
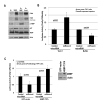
MicroRNAs predominantly decrease gene expression; however, specific mRNAs are translationally upregulated in quiescent (G0) mammalian cells and immature Xenopus laevis oocytes by an FXR1a-associated microRNA-protein complex (microRNP) that lacks the microRNP repressor, GW182. Their mechanism in these conditions of decreased mTOR signaling, and therefore reduced canonical (cap-and-poly(A)-tail-mediated) translation, remains undiscovered. Our data reveal that mTOR inhibition in human THP1 cells enables microRNA-mediated activation. Activation requires shortened/no poly(A)-tail targets; polyadenylated mRNAs are partially activated upon PAIP2 overexpression, which interferes with poly(A)-bound PABP, precluding PABP-enhanced microRNA-mediated inhibition and canonical translation. Consistently, inhibition of PARN deadenylase prevents activation. P97/DAP5, a homolog of canonical translation factor, eIF4G, which lacks PABP- and cap binding complex-interacting domains, is required for activation, and thereby for the oocyte immature state. P97 interacts with 3' UTR-binding FXR1a-associated microRNPs and with PARN, which binds mRNA 5' caps, forming a specialized complex to translate recruited mRNAs in these altered canonical translation conditions.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
FXR1a-associated microRNP: A driver of specialized non-canonical translation in quiescent conditions.RNA Biol. 2017 Feb;14(2):137-145. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1265197. Epub 2016 Dec 2. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 27911187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNP-mediated translational activation of nonadenylated mRNAs in a mammalian cell-free system.Genes Cells. 2018 May;23(5):332-344. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12580. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Genes Cells. 2018. PMID: 29626383
-
Viral and cellular mRNA-specific activators harness PABP and eIF4G to promote translation initiation downstream of cap binding.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jun 13;114(24):6310-6315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1610417114. Epub 2017 May 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28559344 Free PMC article.
-
Interference with interaction between eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4G and poly(A)-binding protein in Xenopus oocytes leads to inhibition of polyadenylated mRNA translation and oocyte maturation.J Biochem. 2001 Dec;130(6):737-40. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a003043. J Biochem. 2001. PMID: 11726272
-
Regulation of poly(A)-binding protein through PABP-interacting proteins.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:537-43. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.061. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381337 Review.
Cited by
-
High-Throughput Analysis Reveals miRNA Upregulating α-2,6-Sialic Acid through Direct miRNA-mRNA Interactions.ACS Cent Sci. 2022 Nov 23;8(11):1527-1536. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.2c00748. Epub 2022 Nov 9. ACS Cent Sci. 2022. PMID: 36439307 Free PMC article.
-
The Function and Regulation Mechanism of Non-Coding RNAs in Muscle Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 26;24(19):14534. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914534. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37833983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA binding protein FXR1-miR301a-3p axis contributes to p21WAF1 degradation in oral cancer.PLoS Genet. 2020 Jan 15;16(1):e1008580. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008580. eCollection 2020 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 31940341 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNAs and Muscle Regeneration: Therapeutic Targets in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 19;22(8):4236. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084236. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33921834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breast Cancer and the Other Non-Coding RNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 23;22(6):3280. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063280. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33807045 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bhattacharyya SN, Habermacher R, Martine U, Closs EI, Filipowicz W. Relief of microRNA-Mediated Translational Repression in Human Cells Subjected to Stress. Cell. 2006;125:1111–1124. - PubMed
-
- Friedman Y, Linial M. miRror2.0: a platform for assessing the joint action of microRNAs in cell regulation. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2013;11:1343012. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

