UBE2T promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis by activating the AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway
- PMID: 26943030
- PMCID: PMC4924777
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7805
UBE2T promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis by activating the AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway
Abstract
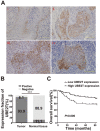
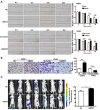
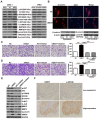
Increasing evidence has shown that UBE2T plays an important role in genomic integrity and carcinogenesis; however, its role in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) has not been investigated. Here, we evaluated the clinicopathological significance of UBE2T in NPC and its underlying mechanisms. Using immunohistochemical analysis of UBE2T expression in NPC samples, we demonstrated that UBE2T is highly expressed in NPC tissues, which correlated with the T/M classification, skull invasion, and poor prognosis. The in vitro assay showed that UBE2T overexpression promoted proliferation, migration, and invasion of NPC cells, while UBE2T knockdown inhibited these processes. Consistent with our in vitro results, in vivo studies indicated that UBE2T overexpression promoted the growth of NPC xenografts and NPC cell metastasis. We found that UBE2T overexpression activated, whereas UBE2T knockdown inhibited, the AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway. Moreover, the pathway-activation and in vitro pro-metastasis effects of UBE2T were blocked by the AKT inhibitor, MK-2206 2HCl. Additionally, UBE2T and p-GSK3 β co-expressed in NPC samples by serial section, and their expressions are correlated. Collectively, our findings demonstrated that UBE2T is a possible diagnostic/prognostic biomarker for NPC and may promote the development and progression of NPC by activating the AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway. Thus, UBE2T could serve as an alternative target for the treatment of NPC.
Keywords: AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway; UBE2T; metastasis; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have disclosed no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Upregulated TRIM29 promotes proliferation and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via PTEN/AKT/mTOR signal pathway.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 22;7(12):13634-50. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7215. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26872369 Free PMC article.
-
DOC-2/DAB2 interactive protein regulates proliferation and mobility of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by targeting PI3K/Akt pathway.Oncol Rep. 2017 Jul;38(1):317-324. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5704. Epub 2017 Jun 6. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28586035
-
Deficiency of pigment epithelium-derived factor in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells triggers the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Jun 1;8(6):e2838. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.114. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28569772 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory role of miRNAs in nasopharyngeal cancer involving PTEN/PI3K/AKT, TGFβ/SMAD, RAS/MAPK, Wnt/β-catenin and pRB-E2F signaling pathways: A review.Cell Biochem Funct. 2024 Mar;42(2):e3945. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3945. Cell Biochem Funct. 2024. PMID: 38362935 Review.
-
Expression of chemokine receptor CXCR4 is closely correlated with clinical outcome in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2016 May;37(5):6099-105. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4464-1. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26611644
Cited by
-
The interplay of UBE2T and Mule in regulating Wnt/β-catenin activation to promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Feb 1;12(2):148. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03403-6. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33542213 Free PMC article.
-
miR-340 Promotes Retinoblastoma Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion Through Targeting WIF1.Onco Targets Ther. 2021 Jun 4;14:3635-3648. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S302800. eCollection 2021. Onco Targets Ther. 2021. PMID: 34113129 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of novel affibody molecules targeting the EBV LMP2A N-terminal domain with inhibiting effects on the proliferation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Apr 1;11(4):213. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2410-7. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32238802 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations and molecular targeting of the GSK-3 regulator, PI3K, in head and neck cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2020 Jun;1867(6):118679. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118679. Epub 2020 Feb 19. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32061630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Molecular Basis of Ubiquitin-Conjugating Enzymes (E2s) as a Potential Target for Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 26;22(7):3440. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073440. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33810518 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lin DC, Meng X, Hazawa M, Nagate Y, Varela AM, Xu L, Sato Y, Liu LZ, Ding YW, Sharma A, Goh BC, Lee SC, Petersson BF, et al. The genomic landscape of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2014;46:866–871. - PubMed
-
- He ML, Luo MX, Lin MC, Kung HF. MicroRNAs: potential diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets for EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1825:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Razak AR, Siu LL, Liu FF, Ito E, O'Sullivan B, Chan K. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: the next challenges. Eur J Cancer. 2010;46:1967–1978. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

