Onto better TRAILs for cancer treatment
- PMID: 26943322
- PMCID: PMC4832109
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2015.174
Onto better TRAILs for cancer treatment
Abstract
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), also known as Apo-2 ligand (Apo2L), is a member of the TNF cytokine superfamily. By cross-linking TRAIL-Receptor (TRAIL-R) 1 or TRAIL-R2, also known as death receptors 4 and 5 (DR4 and DR5), TRAIL has the capability to induce apoptosis in a wide variety of tumor cells while sparing vital normal cells. The discovery of this unique property among TNF superfamily members laid the foundation for testing the clinical potential of TRAIL-R-targeting therapies in the cancer clinic. To date, two of these therapeutic strategies have been tested clinically: (i) recombinant human TRAIL and (ii) antibodies directed against TRAIL-R1 or TRAIL-R2. Unfortunately, however, these TRAIL-R agonists have basically failed as most human tumors are resistant to apoptosis induction by them. It recently emerged that this is largely due to the poor agonistic activity of these agents. Consequently, novel TRAIL-R-targeting agents with increased bioactivity are currently being developed with the aim of rendering TRAIL-based therapies more active. This review summarizes these second-generation novel formulations of TRAIL and other TRAIL-R agonists, which exhibit enhanced cytotoxic capacity toward cancer cells, thereby providing the potential of being more effective when applied clinically than first-generation TRAIL-R agonists.
Conflict of interest statement
AA and LM-L have filed a patent application (W02011020933) for the use of liposome-bound Apo2L/TRAIL. HW is a co-founder and shareholder of Apogenix GmbH, Heidelberg, Germany, and a named inventor on the patent that underlies the development of the TRAIL-R2-specific antibody Conatumumab. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
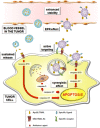
References
-
- Melero I, Berman DM, Aznar MA, Korman AJ, Gracia JLP, Haanen J. Evolving synergistic combinations of targeted immunotherapies to combat cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2015; 15: 457–472. - PubMed
-
- Bremer E, de Bruyn M, Wajant H, Helfrich W. Targeted cancer immunotherapy using ligands of the tumor necrosis factor super-family. Curr Drug Targets 2009; 10: 94–103. - PubMed
-
- Gasparini C, Vecchi Brumatti L, Monasta L, Zauli G. TRAIL-based therapeutic approaches for the treatment of pediatric malignancies. Curr Med Chem 2013; 20: 2254–2271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

