Obstructive jaundice caused by a giant liver hemangioma with Kasabach-Merritt syndrome: a case report
- PMID: 26943417
- PMCID: PMC4595412
- DOI: 10.1186/s40792-015-0095-4
Obstructive jaundice caused by a giant liver hemangioma with Kasabach-Merritt syndrome: a case report
Abstract
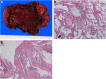
Hemangioma is the most common benign tumor of the liver. Liver hemangioma (LH) usually remains asymptomatic, but the most common symptoms associated with LH are abdominal pain and discomfort. LH is an uncommon cause of bile duct dilatation and obstructive jaundice. An 83-year-old Japanese woman who received hemodialysis at another hospital was referred to our hospital because of abnormal liver function and obstructive jaundice. Abdominal computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging revealed a 13-cm tumor in liver segments IV-V and intrahepatic bile duct dilatation. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography revealed extrinsic compression of the bile duct at the hepatic hilar region. Laboratory tests showed that the patient had low platelet counts and low fibrinogen levels. Because the patient had hyperbilirubinemia and Kasabach-Merritt syndrome, we performed a segmentectomy of liver segments IV and V. Histological examination showed hemangioma of the liver. The patient's thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy improved immediately after surgery. In conclusion, LH is a very rare cause of obstructive jaundice. LH has the potential to compress the bile duct and cause obstructive jaundice.
Keywords: Biliary stricture; Hemangioma; Kasabach-Merritt syndrome; Obstructive jaundice.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

