Diagnostic and prognostic relevance of circulating exosomal miR-373, miR-200a, miR-200b and miR-200c in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer
- PMID: 26943577
- PMCID: PMC4941360
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7850
Diagnostic and prognostic relevance of circulating exosomal miR-373, miR-200a, miR-200b and miR-200c in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer
Abstract
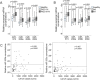
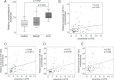
Exosomes are membrane vesicles that mediate intercellular communication by transporting their molecular cargo from cell to cell. We investigated whether serum levels of exosomal miR-373, miR-200a, miR-200b and miR-200c and circulating exosomes have diagnostic and prognostic relevance in a cohort of 163 epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) patients using TaqMan MicroRNA assays and ELISA. The serum concentrations of exosomal miR-373 (p = 0.0001), miR-200a (p = 0.0001), miR-200b (p = 0.0001) and miR-200c (p = 0.028) were significantly higher in EOC patients than healthy women. The levels of miR-200a (p = 0.0001), miR-200b (p = 0.0001) and miR-200c (p = 0.019) could distinguish between malignant and benign ovarian tumors. While the levels of miR-373 and miR-200a were increased in all FIGO/lymph node stages (p = 0.0001), the levels of miR-200b and miR-200c were higher in patients with FIGO stage III-IV (p = 0.0001, p = 0.008, respectively) including lymph node metastasis (p = 0.0001, p = 0.004, respectively) than FIGO stages I-II. The increased levels of miR-200b and miR-200c were also associated with CA125 values (p = 0.0001, p = 0.0001, respectively) and a shorter overall survival (p = 0.007, p = 0.017, respectively). The levels of exosomes were excessively elevated in EOC patients (p = 0.0001). In all three cohorts, they were positively associated with the serum levels of exosomal miR-373 (p = 0.004), miR-200a (p = 0.0001), miR-200b (p = 0.0001) and miR-200c (p = 0.008). In conclusion, the increased levels of exosomal miR-200b and miR-200c mainly observed in advanced EOC suggest that these microRNAs may be involved in tumor progression. The high concentrations of exosomes in EOC patients imply an excessive, active exosomal secretion in EOC.
Keywords: diagnosis; epithelial ovarian cancer; exosomal miRNAs; exosomes; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression of serum miR-200a, miR-200b, and miR-200c as candidate biomarkers in epithelial ovarian cancer and their association with clinicopathological features.Clin Transl Oncol. 2015 Oct;17(10):779-87. doi: 10.1007/s12094-015-1303-1. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Clin Transl Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26063644
-
Circulating Cell-Free miR-373, miR-200a, miR-200b and miR-200c in Patients with Epithelial Ovarian Cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;924:3-8. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-42044-8_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27753009
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic implications of the miR-200 family in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Apr 15;7(5):2392-401. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24966949 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-200a/c as potential biomarker in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC): evidence based on miRNA meta-signature and clinical investigations.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 6;7(49):81621-81633. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13154. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27835595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging roles and therapeutic potential of exosomes in epithelial ovarian cancer.Mol Cancer. 2017 May 15;16(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0659-y. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28506269 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of candidate biomarkers and analysis of prognostic values in ovarian cancer by integrated bioinformatics analysis.Med Oncol. 2016 Nov;33(11):130. doi: 10.1007/s12032-016-0840-y. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Med Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27757782
-
Serum Exosomes and Their miRNA Load-A Potential Biomarker of Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 18;13(6):1373. doi: 10.3390/cancers13061373. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical significance of exosomes as potential biomarkers in cancer.World J Clin Cases. 2019 Jan 26;7(2):171-190. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i2.171. World J Clin Cases. 2019. PMID: 30705894 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal miR-200 family as serum biomarkers for early detection and prognostic prediction of cholangiocarcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019 Oct 1;12(10):3870-3876. eCollection 2019. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31933776 Free PMC article.
-
Serum exosomal microRNA-34a as a potential biomarker in epithelial ovarian cancer.J Ovarian Res. 2020 Apr 26;13(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s13048-020-00648-1. J Ovarian Res. 2020. PMID: 32336272 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simpson RJ, Lim JW, Moritz RL, Mathivanan S. Exosomes: proteomic insights and diagnostic potential. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2009;6:267–283. - PubMed
-
- Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, Sjostrand M, Lee JJ, Lotvall JO. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:654–659. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

