Signal Transduction at the Domain Interface of Prokaryotic Pentameric Ligand-Gated Ion Channels
- PMID: 26943937
- PMCID: PMC4778918
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002393
Signal Transduction at the Domain Interface of Prokaryotic Pentameric Ligand-Gated Ion Channels
Erratum in
-
Correction: Signal Transduction at the Domain Interface of Prokaryotic Pentameric Ligand-Gated Ion Channels.PLoS Biol. 2016 Jun 7;14(6):e1002490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002490. eCollection 2016 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2016. PMID: 27271166 Free PMC article.
Abstract
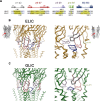
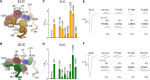
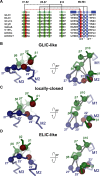
Pentameric ligand-gated ion channels are activated by the binding of agonists to a site distant from the ion conduction path. These membrane proteins consist of distinct ligand-binding and pore domains that interact via an extended interface. Here, we have investigated the role of residues at this interface for channel activation to define critical interactions that couple conformational changes between the two structural units. By characterizing point mutants of the prokaryotic channels ELIC and GLIC by electrophysiology, X-ray crystallography and isothermal titration calorimetry, we have identified conserved residues that, upon mutation, apparently prevent activation but not ligand binding. The positions of nonactivating mutants cluster at a loop within the extracellular domain connecting β-strands 6 and 7 and at a loop joining the pore-forming helix M2 with M3 where they contribute to a densely packed core of the protein. An ionic interaction in the extracellular domain between the turn connecting β-strands 1 and 2 and a residue at the end of β-strand 10 stabilizes a state of the receptor with high affinity for agonists, whereas contacts of this turn to a conserved proline residue in the M2-M3 loop appear to be less important than previously anticipated. When mapping residues with strong functional phenotype on different channel structures, mutual distances are closer in conducting than in nonconducting conformations, consistent with a potential role of contacts in the stabilization of the open state. Our study has revealed a pattern of interactions that are crucial for the relay of conformational changes from the extracellular domain to the pore region of prokaryotic pentameric ligand-gated ion channels. Due to the strong conservation of the interface, these results are relevant for the entire family.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Sine SM, Engel AG. Recent advances in Cys-loop receptor structure and function. Nature. 2006;440(7083):448–55. . - PubMed
-
- Karlin A. On the application of "a plausible model" of allosteric proteins to the receptor for acetylcholine. J Theor Biol. 1967;16(2):306–20. . - PubMed
-
- Edelstein SJ, Changeux JP. Allosteric transitions of the acetylcholine receptor. Adv Protein Chem. 1998;51:121–84. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

