Osteophyte formation and matrix mineralization in a TMJ osteoarthritis mouse model are associated with ectopic hedgehog signaling
- PMID: 26945615
- PMCID: PMC4875867
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matbio.2016.03.001
Osteophyte formation and matrix mineralization in a TMJ osteoarthritis mouse model are associated with ectopic hedgehog signaling
Abstract
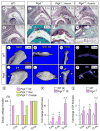
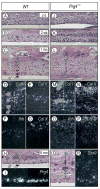
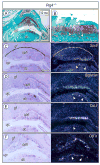
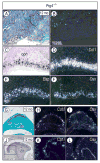
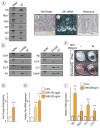
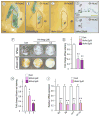
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is a diarthrodial joint that relies on lubricants for frictionless movement and long-term function. It remains unclear what temporal and causal relationships may exist between compromised lubrication and onset and progression of TMJ disease. Here we report that Proteoglycan 4 (Prg4)-null TMJs exhibit irreversible osteoarthritis-like changes over time and are linked to formation of ectopic mineralized tissues and osteophytes in articular disc, mandibular condyle and glenoid fossa. In the presumptive layer of mutant glenoid fossa's articulating surface, numerous chondrogenic cells and/or chondrocytes emerged ectopically within the type I collagen-expressing cell population, underwent endochondral bone formation accompanied by enhanced Ihh expression, became entrapped into temporal bone mineralized matrix, and thereby elicited excessive chondroid bone formation. As the osteophytes grew, the roof of the glenoid fossa/eminence became significantly thicker and flatter, resulting in loss of its characteristic concave shape for accommodation of condyle and disc. Concurrently, the condyles became flatter and larger and exhibited ectopic bone along their neck, likely supporting the enlarged condylar heads. Articular discs lost their concave configuration, and ectopic cartilage developed and articulated with osteophytes. In glenoid fossa cells in culture, hedgehog signaling stimulated chondrocyte maturation and mineralization including alkaline phosphatase, while treatment with hedgehog inhibitor HhAntag prevented such maturation process. In sum, our data indicate that Prg4 is needed for TMJ integrity and long-term postnatal function. In its absence, progenitor cells near presumptive articular layer and disc undergo ectopic chondrogenesis and generate ectopic cartilage, possibly driven by aberrant activation of Hh signaling. The data suggest also that the Prg4-null mice represent a useful model to study TMJ osteoarthritis-like degeneration and clarify its pathogenesis.
Keywords: Heterotopic cartilage; Ihh; Lubricin; Osteophyte; Prg4; TMJ.
Copyright © 2016 International Society of Matrix Biology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Alman BA. The role of hedgehog signalling in skeletal health and disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11:552–60. - PubMed
-
- Arnett GW, Milam SB, Gottesman L. Progressive mandibular retrusion-idiopathic condylar resorption. Part II. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1996;110:117–27. - PubMed
-
- Bakker AC, van de Loo FA, van Beuningen HM, Sime P, van Lent PL, van der Kraan PM, Richards CD, van den Berg WB. Overexpression of active TGF-beta-1 in the murine knee joint: evidence for synovial-layer-dependent chondro-osteophyte formation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001;9:128–36. - PubMed
-
- Beresford WA. Chondroid bone, secondary cartilage and metaplasia. Baltimore, MD, USA: Urban & Schwarzenberg; 1981. pp. 23–47.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

