Cognitive impairments following cranial irradiation can be mitigated by treatment with a tropomyosin receptor kinase B agonist
- PMID: 26946222
- PMCID: PMC4933026
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2016.02.021
Cognitive impairments following cranial irradiation can be mitigated by treatment with a tropomyosin receptor kinase B agonist
Abstract
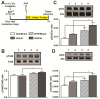
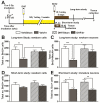
Brain radiotherapy is frequently used successfully to treat brain tumors. However, radiotherapy is often associated with declines in short-term and long-term memory, learning ability, and verbal fluency. We previously identified a downregulation of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) following cranial irradiation in experimental animals. In the present study, we investigated whether targeting the BDNF high affinity receptor, tropomysin receptor kinase B (TrkB), could mitigate radiation-induced cognitive deficits. After irradiation, chronic treatment with a small molecule TrkB agonist, 7,8-dihydroxyflavone (DHF) in mice led to enhanced activation of TrkB and its downstream targets ERK and AKT, both important factors in neuronal development. DHF treatment significantly restored spatial, contextual, and working memory, and the positive effects persisted for at least 3months after completion of the treatment. Consistent with preservation of cognitive functions, chronic DHF treatment mitigated radiation-induced suppression of hippocampal neurogenesis. Spine density and major components of the excitatory synapses, including glutamate receptors and postsynaptic density protein 95 (PSD-95), were also maintained at normal levels by DHF treatment after irradiation. Taken together, our results show that chronic treatment with DHF after irradiation significantly mitigates radiation-induced cognitive defects. This is achieved most likely by preservation of hippocampal neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity.
Keywords: Cognitive function; Hippocampus; Irradiation; Neurogenesis; Synaptic plasticity; TrkB.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Small-molecule TrkB agonist 7,8-dihydroxyflavone reverses cognitive and synaptic plasticity deficits in a rat model of schizophrenia.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2014 Jul;122:30-6. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2014.03.013. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2014. PMID: 24662915
-
A flavonoid agonist of the TrkB receptor for BDNF improves hippocampal neurogenesis and hippocampus-dependent memory in the Ts65Dn mouse model of DS.Exp Neurol. 2017 Dec;298(Pt A):79-96. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.08.018. Epub 2017 Sep 4. Exp Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28882412
-
Activation of TrkB by 7,8-dihydroxyflavone prevents fear memory defects and facilitates amygdalar synaptic plasticity in aging.J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;31(4):765-78. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-120886. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012. PMID: 22710915
-
BDNF-induced local protein synthesis and synaptic plasticity.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt C:639-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23602987 Review.
-
BDNF mechanisms in late LTP formation: A synthesis and breakdown.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt C:664-76. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.06.024. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23831365 Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic Low Dose Neutron Exposure Results in Altered Neurotransmission Properties of the Hippocampus-Prefrontal Cortex Axis in Both Mice and Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 1;22(7):3668. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073668. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33915974 Free PMC article.
-
7,8-Dihydroxyflavone and Neuropsychiatric Disorders: A Translational Perspective from the Mechanism to Drug Development.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022;20(8):1479-1497. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666210915122820. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34525922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation ameliorates cognitive deficits in mice with radiation-induced brain injury by attenuating microglial pyroptosis and promoting neurogenesis via BDNF pathway.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Apr 3;22(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01591-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38570868 Free PMC article.
-
CNS bioavailability and radiation protection of normal hippocampal neurogenesis by a lipophilic Mn porphyrin-based superoxide dismutase mimic, MnTnBuOE-2-PyP5.Redox Biol. 2017 Aug;12:864-871. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.04.027. Epub 2017 Apr 22. Redox Biol. 2017. PMID: 28454069 Free PMC article.
-
7,8-dihydroxyflavone ameliorates motor deficits via regulating autophagy in MPTP-induced mouse model of Parkinson's disease.Cell Death Discov. 2021 Sep 20;7(1):254. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00643-5. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 34545064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acharya MM, Martirosian V, Christie LA, Riparip L, Strnadel J, Parihar VK, Limoli CL. Defining the optimal window for cranial transplantation of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cells to ameliorate radiation-induced cognitive impairment. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(1):74–83. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baker-Andresen D, Flavell CR, Li X, Bredy TW. Activation of BDNF signaling prevents the return of fear in female mice. Learn Mem. 2013;20(5):237–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

