Negative and interactive effects of sex, aging, and alcohol abuse on gray matter morphometry
- PMID: 26947584
- PMCID: PMC4867295
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.23172
Negative and interactive effects of sex, aging, and alcohol abuse on gray matter morphometry
Abstract
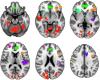
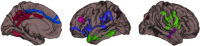
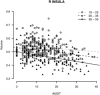
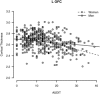
Chronic alcohol use is associated with declines in gray matter (GM) volume, as is the normal aging process. Less apparent, however, is how the interaction between aging and heavy alcohol use affects changes in GM across the lifespan. There is some evidence that women are more vulnerable to the negative effects of alcohol use on GM than men. In the current study, we examined whether localized GM was related to measures of alcohol use disorder (e.g., AUDIT score) in a large sample (N = 436) of participants, ages 18-55 years, with a range of disease severity, using both voxel-based morphometry (VBM) and surface-based morphometry (SBM). We also explored whether GM associations with alcohol use disorder (AUD) severity are moderated by sex and age. Results showed significant negative associations between AUD severity and GM volume throughout temporal, parietal, frontal, and occipital lobes. Women showed more negative effects of alcohol use than men for cortical thickness in left orbitofrontal cortex, but evidence for increased vulnerability based on sex was limited overall. Similarly, a specific age by alcohol use interaction was observed for volume of right insula, but other regional or global interactions were not statistically supported. However, significant negative associations between heavy alcohol use and GM volumes were observed as early as 18-25 years. These findings support that alcohol has deleterious effects on global and regional GM above and beyond age, and, of particular importance, that regional associations emerge in early adulthood. Hum Brain Mapp 37:2276-2292, 2016. © 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: aging; alcohol use disorder; neuroimaging; sex differences; surface-based morphometry; voxel-based morphometry.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Behavioral impulsivity mediates the relationship between decreased frontal gray matter volume and harmful alcohol drinking: A voxel-based morphometry study.J Psychiatr Res. 2016 Dec;83:16-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2016.08.006. Epub 2016 Aug 7. J Psychiatr Res. 2016. PMID: 27529648
-
GATA4 variant interaction with brain limbic structure and relapse risk: A voxel-based morphometry study.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016 Sep;26(9):1431-1437. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2016.06.011. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27397865
-
Lower regional grey matter in alcohol use disorders: evidence from a voxel-based meta-analysis.BMC Psychiatry. 2021 May 11;21(1):247. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03244-9. BMC Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33975595 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical and subcortical gray matter shrinkage in alcohol-use disorders: a voxel-based meta-analysis.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016 Jul;66:92-103. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.03.034. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016. PMID: 27108216 Review.
-
Cortical and Subcortical Gray Matter Volume in Youths With Conduct Problems: A Meta-analysis.JAMA Psychiatry. 2016 Jan;73(1):64-72. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.2423. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26650724 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between empathy and drinking among a community sample of heavy drinkers: Sex differences and neural correlates.Addict Behav. 2022 Sep;132:107346. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2022.107346. Epub 2022 Apr 29. Addict Behav. 2022. PMID: 35533589 Free PMC article.
-
Neural correlates of binocular depth inversion illusion in antipsychotic-naïve first-episode schizophrenia patients.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019 Dec;269(8):897-910. doi: 10.1007/s00406-018-0886-2. Epub 2018 Mar 19. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 29556734
-
Regionally specific gray matter volume is lower in alcohol use disorder: Implications for noninvasive brain stimulation treatment.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021 Aug;45(8):1672-1683. doi: 10.1111/acer.14654. Epub 2021 Aug 2. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021. PMID: 34120347 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte Reactivity and Neurodegeneration in the Female Rat Brain Following Alcohol Dependence.Neuroscience. 2023 Oct 1;529:183-199. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2023.08.016. Epub 2023 Aug 19. Neuroscience. 2023. PMID: 37598836 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between alcohol consumption and gray and white matter volumes in the UK Biobank.Nat Commun. 2022 Mar 4;13(1):1175. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28735-5. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35246521 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akiyama H, Meyer JS, Mortel KF, Terayama Y, Thornby JI, Konno S (1997): Normal human aging: Factors contributing to cerebral atrophy. J Neurol Sci 152:39–49. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2000): Voxel‐based morphometry—The methods. Neuroimage 11:805–821. - PubMed
-
- Beck AT, Steer RA (1993): Beck Anxiety Inventory Manual. San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation.
-
- Beck AT, Steer RA, Brown GK (1996): Manual for the Beck Depression Inventory‐II. San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

