Myocardial Galectin-3 Expression Is Associated with Remodeling of the Pressure-Overloaded Heart and May Delay the Hypertrophic Response without Affecting Survival, Dysfunction, and Cardiac Fibrosis
- PMID: 26948424
- PMCID: PMC4861760
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.12.017
Myocardial Galectin-3 Expression Is Associated with Remodeling of the Pressure-Overloaded Heart and May Delay the Hypertrophic Response without Affecting Survival, Dysfunction, and Cardiac Fibrosis
Abstract
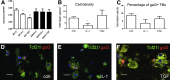
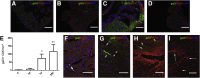
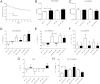
The β-galactoside-binding animal lectin galectin-3 is predominantly expressed by activated macrophages and is a promising biomarker for patients with heart failure. Galectin-3 regulates inflammatory and fibrotic responses; however, its role in cardiac remodeling remains unclear. We hypothesized that galectin-3 may be up-regulated in the pressure-overloaded myocardium and regulate hypertrophy and fibrosis. In normal mouse myocardium, galectin-3 was constitutively expressed in macrophages and was localized in atrial but not ventricular cardiomyocytes. In a mouse model of transverse aortic constriction, galectin-3 expression was markedly up-regulated in the pressure-overloaded myocardium. Early up-regulation of galectin-3 was localized in subpopulations of macrophages and myofibroblasts; however, after 7 to 28 days of transverse aortic constriction, a subset of cardiomyocytes in fibrotic areas contained large amounts of galectin-3. In vitro, cytokine stimulation suppressed galectin-3 synthesis by macrophages and cardiac fibroblasts. Correlation studies revealed that cardiomyocyte- but not macrophage-specific galectin-3 localization was associated with adverse remodeling and dysfunction. Galectin-3 knockout mice exhibited accelerated cardiac hypertrophy after 7 days of pressure overload, whereas female galectin-3 knockouts had delayed dilation after 28 days of transverse aortic constriction. However, galectin-3 loss did not affect survival, systolic and diastolic dysfunction, cardiac fibrosis, and cardiomyocyte hypertrophy in the pressure-overloaded heart. Despite its potential role as a prognostic biomarker, galectin-3 is not a critical modulator of cardiac fibrosis but may delay the hypertrophic response.
Copyright © 2016 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
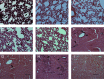
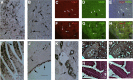
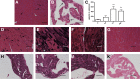
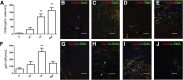
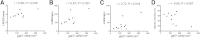


Comment in
-
Galectin-3, Cardiac Function, and Fibrosis.Am J Pathol. 2016 Aug;186(8):2232-2234. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.05.002. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Am J Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27461364
References
-
- Sato S., Hughes R.C. Regulation of secretion and surface expression of Mac-2, a galactoside-binding protein of macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:4424–4430. - PubMed
-
- Kaltner H., Seyrek K., Heck A., Sinowatz F., Gabius H.J. Galectin-1 and galectin-3 in fetal development of bovine respiratory and digestive tracts. Comparison of cell type-specific expression profiles and subcellular localization. Cell Tissue Res. 2002;307:35–46. - PubMed
-
- Rao S.P., Wang Z., Zuberi R.I., Sikora L., Bahaie N.S., Zuraw B.L., Liu F.T., Sriramarao P. Galectin-3 functions as an adhesion molecule to support eosinophil rolling and adhesion under conditions of flow. J Immunol. 2007;179:7800–7807. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

