Cognitive Neurostimulation: Learning to Volitionally Sustain Ventral Tegmental Area Activation
- PMID: 26948894
- PMCID: PMC5074682
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.02.002
Cognitive Neurostimulation: Learning to Volitionally Sustain Ventral Tegmental Area Activation
Abstract
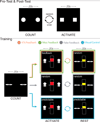
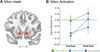
Activation of the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and mesolimbic networks is essential to motivation, performance, and learning. Humans routinely attempt to motivate themselves, with unclear efficacy or impact on VTA networks. Using fMRI, we found untrained participants' motivational strategies failed to consistently activate VTA. After real-time VTA neurofeedback training, however, participants volitionally induced VTA activation without external aids, relative to baseline, Pre-test, and control groups. VTA self-activation was accompanied by increased mesolimbic network connectivity. Among two comparison groups (no neurofeedback, false neurofeedback) and an alternate neurofeedback group (nucleus accumbens), none sustained activation in target regions of interest nor increased VTA functional connectivity. The results comprise two novel demonstrations: learning and generalization after VTA neurofeedback training and the ability to sustain VTA activation without external reward or reward cues. These findings suggest theoretical alignment of ideas about motivation and midbrain physiology and the potential for generalizable interventions to improve performance and learning.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
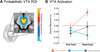
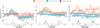

References
-
- Adcock RA, Thangavel A, Whitfield-Gabrieli S, Knutson B, Gabrieli JD. Reward-motivated learning: mesolimbic activation precedes memory formation. Neuron. 2006;50:507–517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

