Molecular mechanism of activation-triggered subunit exchange in Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II
- PMID: 26949248
- PMCID: PMC4859805
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.13405
Molecular mechanism of activation-triggered subunit exchange in Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II
Abstract
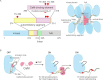
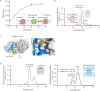
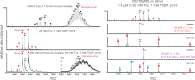
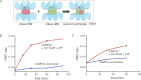
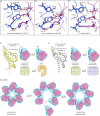
Activation triggers the exchange of subunits in Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), an oligomeric enzyme that is critical for learning, memory, and cardiac function. The mechanism by which subunit exchange occurs remains elusive. We show that the human CaMKII holoenzyme exists in dodecameric and tetradecameric forms, and that the calmodulin (CaM)-binding element of CaMKII can bind to the hub of the holoenzyme and destabilize it to release dimers. The structures of CaMKII from two distantly diverged organisms suggest that the CaM-binding element of activated CaMKII acts as a wedge by docking at intersubunit interfaces in the hub. This converts the hub into a spiral form that can release or gain CaMKII dimers. Our data reveal a three-way competition for the CaM-binding element, whereby phosphorylation biases it towards the hub interface, away from the kinase domain and calmodulin, thus unlocking the ability of activated CaMKII holoenzymes to exchange dimers with unactivated ones.
Keywords: Ca2+/CaM stimulus; E. coli; N. vectensis; S. rosetta; biochemistry; biophysics; kinase activation; structural biology; structural transition; subunit exchange.
Conflict of interest statement
JK: Senior editor,
The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures












References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkóczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung LW, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner R, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, Zwart PH. Phenix: A comprehensive python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallographica. Section D, Biological Crystallography. 2010;66:213–221. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909052925. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berendsen HJC, van der Spoel D, van Drunen R. Gromacs: A message-passing parallel molecular dynamics implementation. Computer Physics Communications. 1995;91:43–56. doi: 10.1016/0010-4655(95)00042-E. - DOI
-
- Bradshaw JM, Kubota Y, Meyer T, Schulman H. An ultrasensitive ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase ii-protein phosphatase 1 switch facilitates specificity in postsynaptic calcium signaling. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2003;100:10512–10517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1932759100. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

