Nanoscale Delivery of Resveratrol towards Enhancement of Supplements and Nutraceuticals
- PMID: 26950147
- PMCID: PMC4808861
- DOI: 10.3390/nu8030131
Nanoscale Delivery of Resveratrol towards Enhancement of Supplements and Nutraceuticals
Abstract
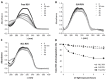
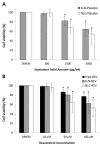
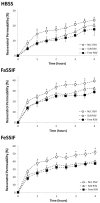
Resveratrol was investigated in terms of its stability, biocompatibility and intestinal permeability across Caco-2 cell monolayers in its free form or encapsulated in solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs). SLNs and NLCs presented a mean diameter between 160 and 190 nm, high negative zeta potential of -30 mV and resveratrol entrapment efficiency of 80%, suggesting they are suitable for resveratrol oral delivery. Nanoencapsulation effectively protected resveratrol from photodegradation, and MTT assays demonstrated that neither resveratrol nor lipid nanoparticles adversely affected cell viability and integrity of Caco-2 cell monolayers. The in vitro intestinal permeability of resveratrol was significantly increased by NLCs, and SLNs did not impair the absorption of resveratrol. Resveratrol oral absorption can be enhanced during meals, since the intestinal permeability was increased in the presence of fed-state intestinal juices. SLNs and NLCs constitute carrier systems for resveratrol oral administration, for further use as supplements or nutraceuticals.
Keywords: biocompatibility; intestinal permeability; lipid nanoparticles; nanodelivery systems; oral bioavailability; resveratrol.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel resveratrol nanodelivery systems based on lipid nanoparticles to enhance its oral bioavailability.Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:177-87. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S37840. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013. PMID: 23326193 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles with Brij78 and TPGS improved in vivo oral bioavailability and in situ intestinal absorption of curcumin.Drug Deliv. 2016;23(2):459-70. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2014.918677. Epub 2014 Jun 3. Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 24892628
-
Size-exclusive effect of nanostructured lipid carriers on oral drug delivery.Int J Pharm. 2016 Sep 10;511(1):524-537. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.07.049. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Int J Pharm. 2016. PMID: 27452421
-
Potential of Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs and NLCs) in Enhancing Oral Bioavailability of Drugs with Poor Intestinal Permeability.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019 Feb 25;20(3):121. doi: 10.1208/s12249-019-1337-8. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019. PMID: 30805893 Review.
-
Nanostructured lipid (NLCs) carriers as a bioavailability enhancement tool for oral administration.Drug Deliv. 2015;22(6):691-700. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2014.898110. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 24670099 Review.
Cited by
-
Phytoglycogen to Enhance the Solubility and in-vitro Permeation of Resveratrol.Food Biophys. 2023 Mar 31:1-10. doi: 10.1007/s11483-023-09785-8. Online ahead of print. Food Biophys. 2023. PMID: 37362010 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan-Based Nanogels Designed for Betanin-Rich Beetroot Extract Transport: Physicochemical and Biological Aspects.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Sep 25;15(19):3875. doi: 10.3390/polym15193875. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835924 Free PMC article.
-
EGCG intestinal absorption and oral bioavailability enhancement using folic acid-functionalized nanostructured lipid carriers.Heliyon. 2019 Jul 3;5(7):e02020. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02020. eCollection 2019 Jul. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31317081 Free PMC article.
-
Controlled Release of Nor-β-lapachone by PLGA Microparticles: A Strategy for Improving Cytotoxicity against Prostate Cancer Cells.Molecules. 2016 Jul 2;21(7):873. doi: 10.3390/molecules21070873. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27384551 Free PMC article.
-
Recent developments in solid lipid nanoparticle and surface-modified solid lipid nanoparticle delivery systems for oral delivery of phyto-bioactive compounds in various chronic diseases.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Mar 15;13:1569-1583. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S155593. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29588585 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Almeida L., Vaz-da-Silva M., Falcao A., Soares E., Costa R., Loureiro A.I., Fernandes-Lopes C., Rocha J.F., Nunes T., Wright L., et al. Pharmacokinetic and safety profile of trans-resveratrol in a rising multiple-dose study in healthy volunteers. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009;53:S7–S15. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200800177. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

