Evaluation of Immune-Related Response Criteria and RECIST v1.1 in Patients With Advanced Melanoma Treated With Pembrolizumab
- PMID: 26951310
- PMCID: PMC5070547
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2015.64.0391
Evaluation of Immune-Related Response Criteria and RECIST v1.1 in Patients With Advanced Melanoma Treated With Pembrolizumab
Abstract
Purpose: We evaluated atypical response patterns and the relationship between overall survival and best overall response measured per immune-related response criteria (irRC) and Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors, version 1.1 (RECIST v1.1) in patients with advanced melanoma treated with pembrolizumab in the phase Ib KEYNOTE-001 study (clinical trial information: NCT01295827).
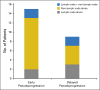
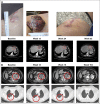
Patients and methods: Patients received pembrolizumab 2 or 10 mg/kg every 2 weeks or every 3 weeks. Atypical responses were identified by using centrally assessed irRC data in patients with ≥ 28 weeks of imaging. Pseudoprogression was defined as ≥ 25% increase in tumor burden at week 12 (early) or any assessment after week 12 (delayed) that was not confirmed as progressive disease at next assessment. Response was assessed centrally per irRC and RECIST v1.1.
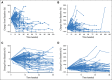
Results: Of the 655 patients with melanoma enrolled, 327 had ≥ 28 weeks of imaging follow-up. Twenty-four (7%) of these 327 patients had atypical responses (15 [5%] with early pseudoprogression and nine [3%] with delayed pseudoprogression). Of the 592 patients who survived ≥ 12 weeks, 84 (14%) experienced progressive disease per RECIST v1.1 but nonprogressive disease per irRC. Two-year overall survival rates were 77.6% in patients with nonprogressive disease per both criteria (n = 331), 37.5% in patients with progressive disease per RECIST v1.1 but nonprogressive disease per irRC (n = 84), and 17.3% in patients with progressive disease per both criteria (n = 177).
Conclusion: Atypical responses were observed in patients with melanoma treated with pembrolizumab. Based on survival analysis, conventional RECIST might underestimate the benefit of pembrolizumab in approximately 15% of patients; modified criteria that permit treatment beyond initial progression per RECIST v1.1 might prevent premature cessation of treatment.
© 2016 by American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest are found in the article online at www.jco.org. Author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures


Comment in
-
Reply to M. Nishino.J Clin Oncol. 2016 Oct 1;34(28):3481. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.69.1097. Epub 2016 Jul 25. J Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27458281 No abstract available.
-
Pseudoprogression and Measurement Variability.J Clin Oncol. 2016 Oct 1;34(28):3480-1. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.67.6759. Epub 2016 Jul 25. J Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27458299 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wolchok JD, Hoos A, O’Day S, et al. Guidelines for the evaluation of immune therapy activity in solid tumors: Immune-related response criteria. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:7412–7420. - PubMed
-
- O’Day SJ, Maio M, Chiarion-Sileni V, et al. Efficacy and safety of ipilimumab monotherapy in patients with pretreated advanced melanoma: A multicenter single-arm phase II study. Ann Oncol. 2010;21:1712–1717. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

