Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis screen to identify pathogenic Lynch syndrome-associated MSH2 DNA mismatch repair gene variants
- PMID: 26951660
- PMCID: PMC4839441
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1520813113
Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis screen to identify pathogenic Lynch syndrome-associated MSH2 DNA mismatch repair gene variants
Abstract
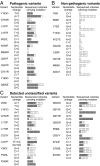
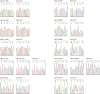
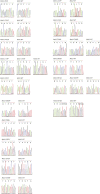
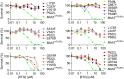
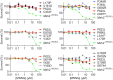
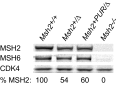
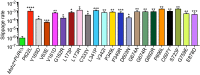
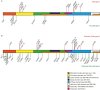
Single-stranded DNA oligonucleotides can achieve targeted base-pair substitution with modest efficiency but high precision. We show that "oligo targeting" can be used effectively to study missense mutations in DNA mismatch repair (MMR) genes. Inherited inactivating mutations in DNA MMR genes are causative for the cancer predisposition Lynch syndrome (LS). Although overtly deleterious mutations in MMR genes can clearly be ascribed as the cause of LS, the functional implications of missense mutations are often unclear. We developed a genetic screen to determine the pathogenicity of these variants of uncertain significance (VUS), focusing on mutator S homolog 2 (MSH2). VUS were introduced into the endogenous Msh2 gene of mouse embryonic stem cells by oligo targeting. Subsequent selection for MMR-deficient cells using the guanine analog 6-thioguanine allowed the detection of MMR-abrogating VUS. The screen was able to distinguish weak and strong pathogenic variants from polymorphisms and was used to investigate 59 Msh2 VUS. Nineteen of the 59 VUS were identified as pathogenic. Functional assays revealed that 14 of the 19 detected variants fully abrogated MMR activity and that five of the detected variants attenuated MMR activity. Implementation of the screen in clinical practice allows proper counseling of mutation carriers and treatment of their tumors.
Keywords: DNA mismatch repair; Lynch syndrome; MSH2; site-directed mutagenesis; variants of uncertain significance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Comment in
-
Enhanced gene targeting to evaluate Lynch syndrome alterations.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Apr 12;113(15):3918-20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1602650113. Epub 2016 Mar 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27035997 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Palombo F, et al. GTBP, a 160-kilodalton protein essential for mismatch-binding activity in human cells. Science. 1995;268(5219):1912–1914. - PubMed
-
- Palombo F, et al. hMutSbeta, a heterodimer of hMSH2 and hMSH3, binds to insertion/deletion loops in DNA. Curr Biol. 1996;6(9):1181–1184. - PubMed
-
- Swann PF, et al. Role of postreplicative DNA mismatch repair in the cytotoxic action of thioguanine. Science. 1996;273(5278):1109–1111. - PubMed
-
- Brown KD, et al. The mismatch repair system is required for S-phase checkpoint activation. Nat Genet. 2003;33(1):80–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

