Unbound Bilirubin and Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder in Late Preterm and Term Infants with Severe Jaundice
- PMID: 26952116
- PMCID: PMC4884491
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.02.024
Unbound Bilirubin and Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder in Late Preterm and Term Infants with Severe Jaundice
Abstract
Objective: This study evaluates whether unbound bilirubin is a better predictor of auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder (ANSD) than total serum bilirubin (TSB) or the bilirubin:albumin molar ratio (BAMR) in late preterm and term neonates with severe jaundice (TSB ≥20 mg/dL or TSB that met exchange transfusion criteria).
Study design: Infants ≥34 weeks' gestation with severe jaundice during the first 2 weeks of life were eligible for the prospective observational study. A comprehensive auditory evaluation was performed within 72 hours of peak TSB. ANSD was defined as absent or abnormal auditory brainstem evoked response waveform morphology at 80-decibel click intensity in the presence of normal outer hair cell function. TSB, serum albumin, and unbound bilirubin were measured using the colorimetric, bromocresol green, and modified peroxidase method, respectively.
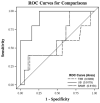
Results: Five of 44 infants developed ANSD. By logistic regression, peak unbound bilirubin but not peak TSB or peak BAMR was associated with ANSD (OR, 4.6; 95% CI, 1.6-13.5; P = .002). On comparing receiver operating characteristic curves, the area under the curve for unbound bilirubin (0.92) was significantly greater (P = .04) compared with the area under the curve for TSB (0.50) or BAMR (0.62).
Conclusions: Unbound bilirubin is a more sensitive and specific predictor of ANSD than TSB or BAMR in late preterm and term infants with severe jaundice.
Keywords: Total serum bilirubin; bilirubin-induced neurotoxicity; bilirubin:albumin molar ratio; sensitivity; specificity.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Measurement of Circulating Unbound Bilirubin: Will It Ever Be a Part of Routine Neonatal Care?J Pediatr. 2016 Jun;173:6-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.03.044. Epub 2016 Apr 7. J Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27063804 No abstract available.
References
-
- Burgos AE, Schmitt SK, Stevenson DK, Phibbs CS. Readmission for neonatal jaundice in California, 1991-2000: trends and implications. Pediatrics. 2008;121:e864–9. - PubMed
-
- From the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Kernicterus in full-term infants--United States, 1994-1998. Jama. 2001;286:299–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

