Developmental origin of lung macrophage diversity
- PMID: 26952982
- PMCID: PMC4852511
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.129122
Developmental origin of lung macrophage diversity
Abstract
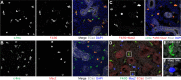
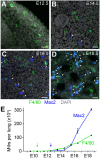
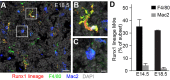
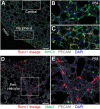
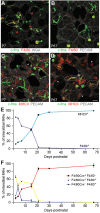
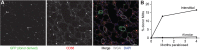
Macrophages are specialized phagocytic cells, present in all tissues, which engulf and digest pathogens, infected and dying cells, and debris, and can recruit and regulate other immune cells and the inflammatory response and aid in tissue repair. Macrophage subpopulations play distinct roles in these processes and in disease, and are typically recognized by differences in marker expression, immune function, or tissue of residency. Although macrophage subpopulations in the brain have been found to have distinct developmental origins, the extent to which development contributes to macrophage diversity between tissues and within tissues is not well understood. Here, we investigate the development and maintenance of mouse lung macrophages by marker expression patterns, genetic lineage tracing and parabiosis. We show that macrophages populate the lung in three developmental waves, each giving rise to a distinct lineage. These lineages express different markers, reside in different locations, renew in different ways, and show little or no interconversion. Thus, development contributes significantly to lung macrophage diversity and targets each lineage to a different anatomical domain.
Keywords: Lineage tracing; Lung development; Lung macrophage; Parabiosis; Phagocytosis.
© 2016. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Bedoret D., Wallemacq H., Marichal T., Desmet C., Quesada Calvo F., Henry E., Closset R., Dewals B., Thielen C., Gustin P. et al. (2009). Lung interstitial macrophages alter dendritic cell functions to prevent airway allergy in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 119, 3723-3738. 10.1172/JCI39717 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blussé van Oud Alblas A., van der Linden-Schrever B. and van Furth R. (1981). Origin and kinetics of pulmonary macrophages during an inflammatory reaction induced by intravenous administration of heat-killed bacillus Calmette-Guerin. J. Exp. Med. 154, 235-252. 10.1084/jem.154.2.235 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bowden D. H., Adamson I. Y., Grantham W. G. and Wyatt J. P. (1969). Origin of the lung macrophage. Evidence derived from radiation injury. Arch. Pathol. 88, 540-546. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

