Diabetes and Prediabetes and Risk of Hospitalization: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study
- PMID: 26953170
- PMCID: PMC4839170
- DOI: 10.2337/dc15-1335
Diabetes and Prediabetes and Risk of Hospitalization: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study
Abstract
Objective: To examine the magnitude and types of hospitalizations among persons with prediabetes, undiagnosed diabetes, and diagnosed diabetes.
Research design and methods: This study included 13,522 participants in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study (mean age 57 years, 56% female, 24% black, 18% with prediabetes, 4% with undiagnosed diabetes, 9% with diagnosed diabetes) with follow-up in 1990-2011 for hospitalizations. Participants were categorized by diabetes/HbA1c status: without diagnosed diabetes, HbA1c <5.7% (reference); prediabetes, 5.7 to <6.5%; undiagnosed diabetes, ≥6.5%; and diagnosed diabetes, <7.0 and ≥7.0%.
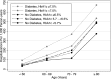
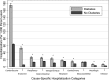
Results: Demographic adjusted rates per 1,000 person-years of all-cause hospitalizations were higher with increasing diabetes/HbA1c category (Ptrend < 0.001). Persons with diagnosed diabetes and HbA1c ≥7.0% had the highest rates of hospitalization (3.1 times higher than those without a history of diagnosed diabetes, HbA1c <5.7%, and 1.5 times higher than those with diagnosed diabetes, HbA1c <7.0%, P < 0.001 for both comparisons). Persons with undiagnosed diabetes had 1.6 times higher rates of hospitalization and those with prediabetes had 1.3 times higher rates of hospitalization than those without diabetes and HbA1c <5.7% (P < 0.001 for both comparisons). Rates of hospitalization by diabetes/HbA1c category were different by race (Pinteraction = 0.011) and by sex (Pinteraction = 0.020). There were significantly excess rates of hospitalizations due to cardiovascular, endocrine, respiratory, gastrointestinal, iatrogenic/injury, neoplasm, genitourinary, neurologic, and infection causes among those with diagnosed diabetes compared with those without a history of diagnosed diabetes (all P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Persons with diagnosed diabetes, undiagnosed diabetes, and prediabetes are at a significantly elevated risk of hospitalization compared with those without diabetes. Substantial excess rates of hospitalizations in persons with diagnosed diabetes were for endocrine, infection, and iatrogenic/injury causes, which may be preventable with improved diabetes care.
© 2016 by the American Diabetes Association. Readers may use this article as long as the work is properly cited, the use is educational and not for profit, and the work is not altered.
Figures
References
-
- Dall TM, Yang W, Halder P, et al. . The economic burden of elevated blood glucose levels in 2012: diagnosed and undiagnosed diabetes, gestational diabetes mellitus, and prediabetes. Diabetes Care 2014;37:3172–3179 - PubMed
-
- Dall TM, Zhang Y, Chen YJ, Quick WW, Yang WG, Fogli J. The economic burden of diabetes. Health Aff (Millwood) 2010;29:297–303 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK089174/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007024/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK106414/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

