Mitochondria in pluripotent stem cells: stemness regulators and disease targets
- PMID: 26953561
- PMCID: PMC5011451
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gde.2016.02.001
Mitochondria in pluripotent stem cells: stemness regulators and disease targets
Abstract
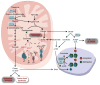
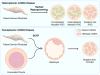
Beyond their canonical role in efficient ATP production through oxidative metabolism, mitochondria are increasingly recognized as critical in defining stem cell function and fate. Implicating a fundamental interplay within the epigenetics of eukaryotic cell systems, the integrity of mitochondria is found vital across the developmental/differentiation spectrum from securing pluripotency maintenance to informing organotypic decisions. This overview will discuss recent progress on examining the plasticity of mitochondria in enabling the execution of programming and reprogramming regimens, as well as the application of nuclear reprogramming and somatic cell nuclear transfer as rescue techniques to generate genetically and functionally corrected pluripotent stem cells from patients with mitochondrial DNA-based disease.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126:663–676. - PubMed
-
- Folmes CD, Nelson TJ, Martinez-Fernandez A, Arrell DK, Lindor JZ, Dzeja PP, Ikeda Y, Perez-Terzic C, Terzic A. Somatic oxidative bioenergetics transitions into pluripotency-dependent glycolysis to facilitate nuclear reprogramming. Cell Metab. 2011;14:264–271. Nuclear reprogramming induces mitochondrial and metabolic remodeling resulting in a metabolic shift from oxidative metabolism to glycolysis. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Prigione A, Fauler B, Lurz R, Lehrach H, Adjaye J. The senescence-related mitochondrial/oxidative stress pathway is repressed in human induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells. 2010;28:721–733. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

