Exercise: a "new drug" for elderly patients with chronic heart failure
- PMID: 26953895
- PMCID: PMC4931840
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.100901
Exercise: a "new drug" for elderly patients with chronic heart failure
Abstract
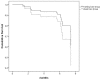
Patients with chronic heart failure (CHF) experience progressive deterioration of functional capacity and quality of life (QoL). This prospective, randomized, controlled trial assesses the effect of exercise training (ET) protocol on functional capacity, rehospitalization, and QoL in CHF patients older than 70 years compared with a control group. A total of 343 elderly patients with stable CHF (age, 76.90±5.67, men, 195, 56.9%) were randomized to ET (TCG, n=170) or usual care (UCG, n=173). The ET protocol involved supervised training sessions for 3 months in the hospital followed by home-telemonitored sessions for 3 months. Assessments, performed at baseline and at 3 and 6 months, included: ECG, resting echocardiography, NT-proBNP, 6-minute walk test (6MWT), Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire, and comprehensive geriatric assessment with the InterRAI-HC instrument. As compared to UCG, ET patients at 6 months showed: i) significantly increased 6MWT distance (450±83 vs. 290±97 m, p=0.001); ii) increased ADL scores (5.00±2.49 vs. 6.94±5.66, p=0.037); iii) 40% reduced risk of rehospitalisation (hazard ratio=0.558, 95%CI, 0.326-0.954, p=0.033); and iv) significantly improved perceived QoL (28.6±12.3 vs. 44.5±12.3, p=0.001). In hospital and home-based telemonitored exercise confer significant benefits on the oldest CHF patients, improving functional capacity and subjective QoL and reducing risk of rehospitalisation.
Keywords: 6MWT; QoL; chronic heart failure; elderly CHF patients; physical exercise; quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Figures

References
-
- McMurray JJ, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, Auricchio A, Böhm M, Dickstein K, Falk V, Filippatos G, Fonseca C, Gomez-Sanchez MA, Jaarsma T, Køber L, Lip GY, Maggioni AP, Parkhomenko A, Pieske BM, et al. ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail. 2012;14:803–869. - PubMed
-
- Schocken DD. Epidemiology and risk factors for heart failure in the elderly. Clin Geriatr Med. 2000;16:407–418. - PubMed
-
- Kalogeropoulos A, Georgiopoulou V, Kritchevsky SB, Psaty BM, Smith NL, Newman AB, Rodondi N, Satterfield S, Bauer DC, Bibbins-Domingo K, Smith AL, Wilson PW, Vasan RS, Harris TB, Butler J. Epidemiology of incident heart failure in a contemporary elderly cohort: the health. aging. and body composition study. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169:708–715. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Piepoli MF, Binno S, Corrà U, Seferovic P, Conraads V, Jaarsma T, Schmid J-P, Filippatos G, Ponikowski PP, on behalf of the Committee on Exercise Physiology & Training of the Heart Failure Associuation of the ESC ExtraHF survey: the first European survey on implementation of exercise training in heart failure patients. European Heart Journal. 2015 doi: 10.1002/ejhf.271. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

