The role of diseases, risk factors and symptoms in the definition of multimorbidity - a systematic review
- PMID: 26954365
- PMCID: PMC4977932
- DOI: 10.3109/02813432.2016.1153242
The role of diseases, risk factors and symptoms in the definition of multimorbidity - a systematic review
Abstract
Objective is to explore how multimorbidity is defined in the scientific literature, with a focus on the roles of diseases, risk factors, and symptoms in the definitions.
Design: Systematic review.
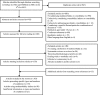
Methods: MEDLINE (PubMed), Embase, and The Cochrane Library were searched for relevant publications up until October 2013. One author extracted the information. Ambiguities were resolved, and consensus reached with one co-author. Outcome measures were: cut-off point for the number of conditions included in the definitions of multimorbidity; setting; data sources; number, kind, duration, and severity of diagnoses, risk factors, and symptoms. We reviewed 163 articles. In 61 articles (37%), the cut-off point for multimorbidity was two or more conditions (diseases, risk factors, or symptoms). The most frequently used setting was the general population (68 articles, 42%), and primary care (41 articles, 25%). Sources of data were primarily self-reports (56 articles, 42%). Out of the 163 articles selected, 115 had individually constructed multimorbidity definitions, and in these articles diseases occurred in all definitions, with diabetes as the most frequent. Risk factors occurred in 98 (85%) and symptoms in 71 (62%) of the definitions. The severity of conditions was used in 26 (23%) of the definitions, but in different ways. The definition of multimorbidity is heterogeneous and risk factors are more often included than symptoms. The severity of conditions is seldom included. Since the number of people living with multimorbidity is increasing there is a need to develop a concept of multimorbidity that is more useful in daily clinical work. Key points The increasing number of multimorbidity patients challenges the healthcare system. The concept of multimorbidity needs further discussion in order to be implemented in daily clinical practice. Many definitions of multimorbidity exist and most often a cut-off point of two or more is applied to a range of 4-147 different conditions. Diseases are included in all definitions of multimorbidity. Risk factors are often included in existing definitions, whereas symptoms and the severity of the conditions are less frequently included.
Keywords: Definition; Denmark; diseases; general practice; multimorbidity; primary care; risk factors; symptoms.
Figures
References
-
- van der Akker M BF, Knottnerus JA.. Comorbidity or multimorbidity: what's in a name? A review of literture. Eur J Gen Pract. 1996;2:65–70.
-
- Uijen AA, van de Lisdonk EH.. Multimorbidity in primary care: prevalence and trend over the last 20 years. Eur J Gen Pract. 2008;14:28–32. - PubMed
-
- Barnett K, Mercer SW, Norbury M, et al. Epidemiology of multimorbidity and implications for health care, research, and medical education: a cross-sectional study. Lancet. 2012;380:37–43. - PubMed
-
- Glynn LG, Valderas JM, Healy P, et al. The prevalence of multimorbidity in primary care and its effect on health care utilization and cost. FamPract. 2011;28:516–523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical