On the selectivity of the Gαq inhibitor UBO-QIC: A comparison with the Gαi inhibitor pertussis toxin
- PMID: 26954502
- PMCID: PMC4839537
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.03.003
On the selectivity of the Gαq inhibitor UBO-QIC: A comparison with the Gαi inhibitor pertussis toxin
Abstract
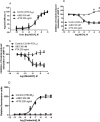
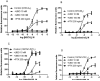
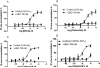
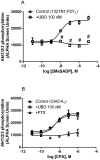
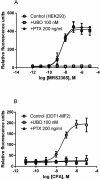
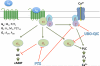
Gαq inhibitor UBO-QIC (FR900359) is becoming an important pharmacological tool, but its selectivity against other G proteins and their subunits, especially βγ, has not been well characterized. We examined UBO-QIC's effect on diverse signaling pathways mediated via various G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and G protein subunits by comparison with known Gαi inhibitor pertussis toxin. As expected, UBO-QIC inhibited Gαq signaling in all assay systems examined. However, other non-Gαq-events, e.g. Gβγ-mediated intracellular calcium release and inositol phosphate production, following activation of Gi-coupled A1 adenosine and M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, were also blocked by low concentrations of UBO-QIC, indicating that its effect is not limited to Gαq. Thus, UBO-QIC also inhibits Gβγ-mediated signaling similarly to pertussis toxin, although UBO-QIC does not affect Gαi-mediated inhibition or Gαs-mediated stimulation of adenylyl cyclase activity. However, the blockade by UBO-QIC of GPCR signaling, such as carbachol- or adenosine-mediated calcium or inositol phosphate increases, does not always indicate inhibition of Gαq-mediated events, as the βγ subunits released from Gi proteins following the activation of Gi-coupled receptors, e.g. M2 and A1Rs, may produce similar signaling events. Furthermore, UBO-QIC completely inhibited Akt signaling, but only partially blocked ERK1/2 activity stimulated by the Gq-coupled P2Y1R. Thus, we have revealed new aspects of the pharmacological interactions of UBO-QIC.
Keywords: FR900359; G protein; GPCR; Gα(q) inhibitor; Gβγ subunits; UBO-QIC.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
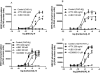

Similar articles
-
Characterization of UBO-QIC as a Gαq inhibitor in platelets.Platelets. 2015;26(8):771-8. doi: 10.3109/09537104.2014.998993. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Platelets. 2015. PMID: 25734215
-
Promiscuous G-Protein-Coupled Receptor Inhibition of Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin 3 Ion Channels by Gβγ Subunits.J Neurosci. 2019 Oct 2;39(40):7840-7852. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0882-19.2019. Epub 2019 Aug 26. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31451581 Free PMC article.
-
G-protein-dependency of orexin/hypocretin receptor signalling in recombinant Chinese hamster ovary cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Aug 5;476(4):379-385. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.05.130. Epub 2016 May 26. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27237973
-
Gaq proteins: molecular pharmacology and therapeutic potential.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Apr;74(8):1379-1390. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2405-9. Epub 2016 Nov 4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 27815595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure, Function, Pharmacology, and Therapeutic Potential of the G Protein, Gα/q,11.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2015 Mar 24;2:14. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2015.00014. eCollection 2015. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2015. PMID: 26664886 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Selective inhibition of histamine-evoked Ca2+ signals by compartmentalized cAMP in human bronchial airway smooth muscle cells.Cell Calcium. 2018 May;71:53-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2017.12.002. Epub 2017 Dec 15. Cell Calcium. 2018. PMID: 29604964 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological profile of the neuropeptide S receptor: Dynamic mass redistribution studies.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2018 Dec 3;6(6):e00445. doi: 10.1002/prp2.445. eCollection 2018 Dec. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2018. PMID: 30534379 Free PMC article.
-
On the G protein-coupling selectivity of the native A2B adenosine receptor.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 May;151:201-213. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.12.003. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29225130 Free PMC article.
-
A2B adenosine receptor-triggered intracellular calcium mobilization: Cell type-dependent involvement of Gi, Gq, Gs proteins and protein kinase C.Purinergic Signal. 2025 Jun;21(3):499-513. doi: 10.1007/s11302-025-10070-1. Epub 2025 Feb 11. Purinergic Signal. 2025. PMID: 39934472 Free PMC article.
-
Protease-activated receptor-2 in endosomes signals persistent pain of irritable bowel syndrome.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Jul 31;115(31):E7438-E7447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1721891115. Epub 2018 Jul 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30012612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fujioka M, Koda S, Morimoto Y, Biemann K. Structure of FR900359, a cyclic depsipeptide from Ardisia crenata sims. J Org Chem. 1988;53(12):2820–5.
-
- Inamdar V, Patel A, Manne BK, Dangelmaier C, Kunapuli SP. Characterization of UBOQIC as a G q inhibitor in platelets. Platelets. 2015;26(8):771–8. - PubMed
-
- Hennen S, Wang H, Peters L, Merten N, Simon K, Spinrath A, Blättermann S, Akkari R, Schrage R, Schröder R, Schulz D, Vermeiren C, Zimmermann K, Kehraus S, Drewke C, Pfeifer A, König GM, Mohr K, Gillard M, Müller CE, Lu QR, Gomeza J, Kostenis E. Decoding signaling and function of the orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR17 with a small-molecule agonist - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

