Silencing Status Epilepticus-Induced BDNF Expression with Herpes Simplex Virus Type-1 Based Amplicon Vectors
- PMID: 26954758
- PMCID: PMC4783051
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150995
Silencing Status Epilepticus-Induced BDNF Expression with Herpes Simplex Virus Type-1 Based Amplicon Vectors
Abstract
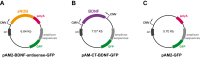
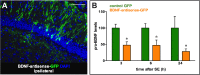
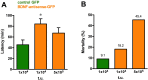
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) has been found to produce pro- but also anti-epileptic effects. Thus, its validity as a therapeutic target must be verified using advanced tools designed to block or to enhance its signal. The aim of this study was to develop tools to silence the BDNF signal. We generated Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) derived amplicon vectors, i.e. viral particles containing a genome of 152 kb constituted of concatameric repetitions of an expression cassette, enabling the expression of the gene of interest in multiple copies. HSV-1 based amplicon vectors are non-pathogenic and have been successfully employed in the past for gene delivery into the brain of living animals. Therefore, amplicon vectors should represent a logical choice for expressing a silencing cassette, which, in multiple copies, is expected to lead to an efficient knock-down of the target gene expression. Here, we employed two amplicon-based BDNF silencing strategies. The first, antisense, has been chosen to target and degrade the cytoplasmic mRNA pool of BDNF, whereas the second, based on the convergent transcription technology, has been chosen to repress transcription at the BDNF gene. Both these amplicon vectors proved to be effective in down-regulating BDNF expression in vitro, in BDNF-expressing mesoangioblast cells. However, only the antisense strategy was effective in vivo, after inoculation in the hippocampus in a model of status epilepticus in which BDNF mRNA levels are strongly increased. Interestingly, the knocking down of BDNF levels induced with BDNF-antisense was sufficient to produce significant behavioral effects, in spite of the fact that it was produced only in a part of a single hippocampus. In conclusion, this study demonstrates a reliable effect of amplicon vectors in knocking down gene expression in vitro and in vivo. Therefore, this approach may find broad applications in neurobiological studies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA amplified as bacterial artificial chromosome in Escherichia coli: rescue of replication-competent virus progeny and packaging of amplicon vectors.Hum Gene Ther. 1998 Dec 10;9(18):2787-94. doi: 10.1089/hum.1998.9.18-2787. Hum Gene Ther. 1998. PMID: 9874276
-
A novel 'piggyback' packaging system for herpes simplex virus amplicon vectors.Hum Gene Ther. 1996 Oct 20;7(16):2003-13. doi: 10.1089/hum.1996.7.16-2003. Hum Gene Ther. 1996. PMID: 8930661
-
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1)-derived amplicon vectors.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1144:81-98. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0428-0_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24671678
-
Progress and prospects: biological properties and technological advances of herpes simplex virus type 1-based amplicon vectors.Gene Ther. 2009 Jun;16(6):709-15. doi: 10.1038/gt.2009.42. Epub 2009 Apr 16. Gene Ther. 2009. PMID: 19369969 Review.
-
HSV-1-derived amplicon vectors: recent technological improvements and remaining difficulties--a review.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2009 May;104(3):399-410. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02762009000300002. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2009. PMID: 19547864 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene Therapy Tools for Brain Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jul 1;10:724. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00724. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31312139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improvement of HSV-1 based amplicon vectors for a safe and long-lasting gene therapy in non-replicating cells.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2021 Mar 29;21:399-412. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2021.03.020. eCollection 2021 Jun 11. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2021. PMID: 33869657 Free PMC article.
-
New Tools for Epilepsy Therapy.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 May 29;12:147. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00147. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29896092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-replicative herpes simplex virus genomic and amplicon vectors for gene therapy - an update.Gene Ther. 2025 May;32(3):173-183. doi: 10.1038/s41434-024-00500-x. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Gene Ther. 2025. PMID: 39533042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Personalized Needles for Microinjections in the Rodent Brain.J Vis Exp. 2018 Jan 24;(131):55751. doi: 10.3791/55751. J Vis Exp. 2018. PMID: 29443027 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simonato M, Tongiorgi E, Kokaia M. Angels and demons: neurotrophic factors and epilepsy. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2006;27: 631–638. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

