Elective surgery cancelation on day of surgery: An endless dilemma
- PMID: 26955314
- PMCID: PMC4760047
- DOI: 10.4103/1658-354X.169479
Elective surgery cancelation on day of surgery: An endless dilemma
Abstract
Background: Cancelation of surgery is a constant agonizing dilemma for nearly all healthcare services that has been intensively investigated to find out its roots, consequences, and possible solutions. The rates of cancelation of surgery vary between centers and more so among surgical specialties with numerous reasons standing behind this phenomenon.
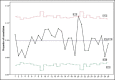
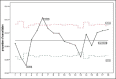
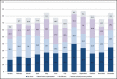
Patients and methods: In the current study, analysis of monthly cancelation rates from January 2009 to December 2012, and assessment of establishing new operating rooms (ORs) using statistical process control charts was conducted. A detailed review of a total of 1813 cases canceled on the day of surgery from January to December 2012, to examine the various reasons of cancelation among surgical specialties.
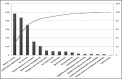
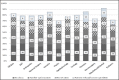
Results: The average cancelation rate was 11.1%, which dropped to 9.0% after launching of new theaters. Four reasons explained about 80% of cancelations; Patients "no show" was the leading cause of cancelation (27%). One-fourth of cancelations (24.3%) were due to the need for further optimization, and the third most prominent cause of cancelation was a lack of OR time (19.5%). Unavailability of staff/equipment/implants accounted for only 0.7% of cancelations. The no show was the most common cause of cancelation among all surgical specialties ranging from 21% for plastic surgery to 32% in ophthalmic surgeries.
Conclusion: It was confirmed that there is a unique profile of cancelation of surgery problem for every institute, an extension of infrastructure may not be the only solution. Control charts helped to enhance the general picture and are functional in monitoring and evaluating changes in the cancelation of surgery.
Keywords: Cancelation of surgery; Saudi Arabia; Statistical process control.
Figures
References
-
- Trentman T, Mueller J, Fassett S, Dormer C, Weinmeister K. Day of surgery cancellations in a tertiary care hospital: A one year review. J Anesth Clin Res. 2010;1:2.
-
- Schofield WN, Rubin GL, Piza M, Lai YY, Sindhusake D, Fearnside MR, et al. Cancellation of operations on the day of intended surgery at a major Australian referral hospital. Med J Aust. 2005;182:612–5. - PubMed
-
- Jim’Enez A, Artigas C, Elia M, Casamayor C, Gracia J, Mart’Inez M. Cancellations in ambulatory day surgery: An observational study. Ambul Surg. 2006;12:119–23.
-
- Laisi J, Tohmo H, Keränen U. Surgery cancelation on the day of surgery in same-day admission in a Finnish hospital. Scand J Surg. 2013;102:204–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

