Nickel chloride (NiCl2) induces endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress by activating UPR pathways in the kidney of broiler chickens
- PMID: 26956054
- PMCID: PMC4951229
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7919
Nickel chloride (NiCl2) induces endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress by activating UPR pathways in the kidney of broiler chickens
Abstract
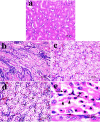
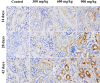
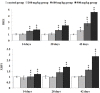
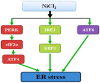
It has been known that overexposure to Ni can induce nephrotoxicity. However, the mechanisms of underlying Ni nephrotoxicity are still elusive, and also Ni- and Ni compound-induced ER stress has been not reported in vivo at present. Our aim was to use broiler chickens as animal model to test whether the ER stress was induced and UPR was activated by NiCl2 in the kidney using histopathology, immunohistochemistry and qRT-PCR. Two hundred and eighty one-day-old broiler chickens were divided into 4 groups and fed on a control diet and the same basal diet supplemented with 300 mg/kg, 600mg/kg and 900mg/kg of NiCl2 for 42 days. We found that dietary NiCl2 in excess of 300 mg/kg induced ER stress, which was characterized by increasing protein and mRNA expression of ER stress markers, e.g., GRP78 and GRP94. Concurrently, all the three UPR pathways were activated by dietary NiCl2. Firstly, the PERK pathway was activated by increasing eIF2a and ATF4 mRNA expression. Secondly, the IRE1 pathway was activated duo to increase in IRE1 and XBP1 mRNA expression. And thirdly, the increase of ATF6 mRNA expression suggested that ATF6 pathway was activated. The findings clearly demonstrate that NiCl2 induces the ER stress through activating PERK, IRE1 and ATF6 UPR pathways, which is proved to be a kind of molecular mechanism of Ni- or/and Ni compound-induced nephrotoxicity.
Keywords: ER stress; IRE1; Immune response; Immunity; Immunology and Microbiology Section; NiCl2; PERK; UPR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Chau Y, Kulikovsky-Cordeiro O. Occurrence of nickel in the Canadian environment. Environ Rev. 1995;3:95–120.
-
- Henderson RG, Durando J, Oller AR, Merkel DJ, Marone PA, Bates HK. Acute oral toxicity of nickel compounds. Regul Toxicol Pharm. 2012;62:425–432. - PubMed
-
- Xu S, He M, Zhong M, Li L, Lu Y, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Yu Z, Zhou Z. The neuroprotective effects of taurine against nickel by reducing oxidative stress and maintaining mitochondrial function in cortical neurons. Neurosci Lett. 2015;590:52–57. - PubMed
-
- Gathwan KH, Al-Karkhi IHT, Jaffar Al-Mulla EA. Hepatic toxicity of nickel chloride in mice. Res Chem Intermed. 2012;39:2537–2542.
-
- Scutariu MD, Ciupilan C. Nickel and magnesium effects in the rat kidney, treated with acid retinoic. Comparative study. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 2007;111:744–747. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

