Azilsartan compared to ACE inhibitors in anti-hypertensive therapy: one-year outcomes of the observational EARLY registry
- PMID: 26956148
- PMCID: PMC4784379
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-016-0222-6
Azilsartan compared to ACE inhibitors in anti-hypertensive therapy: one-year outcomes of the observational EARLY registry
Abstract
Background: Azilsartan medoxomil (AZL-M), has been demonstrated to be more effective than the other sartans currently in use; however, there is insufficient information available comparing it with ACE-inhibitors. Therefore, we aimed to compare the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of AZL-M with that of ACE-inhibitors in a real life clinical setting.
Methods: The EARLY registry is a prospective, observational, national, multicentre registry with a follow-up period of 12 months. There were two principal objectives: 1) documentation of the achievement of target BP values set according to recent national and international guidelines, and 2) description of the safety profile of AZL-M.
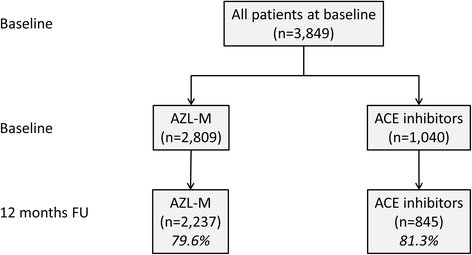
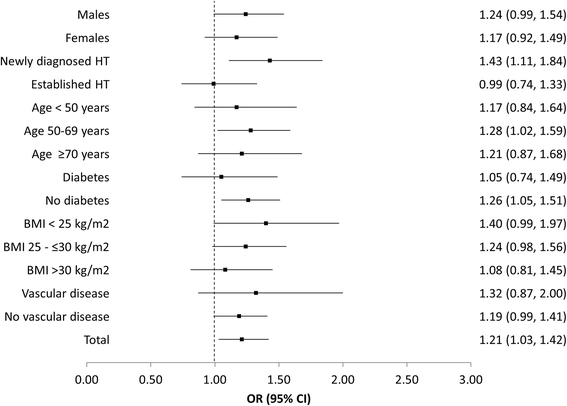
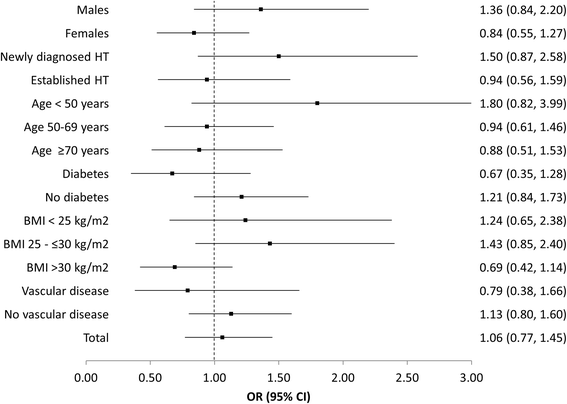
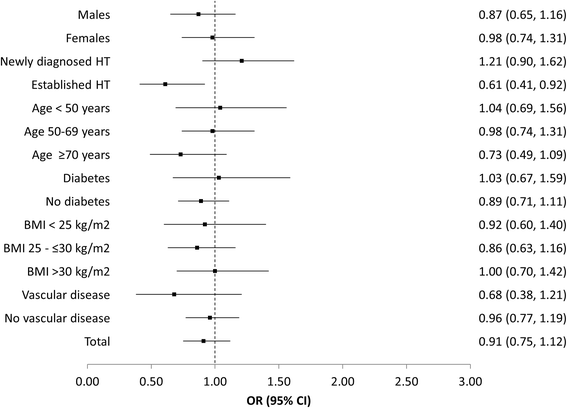
Results: A total of 3 849 patients with essential arterial hypertension were recruited from primary care offices in Germany. Patients who initiated monotherapy at baseline comprising either AZL-M or an ACE-inhibitor were included at a ratio of seven to three. Results demonstrated that a blood pressure target of <140/90 mmHg was achieved by a significantly greater proportion of patients in the AZL-M group (61.1 %) compared with the ACE-inhibitor group (56.4 %; p < 0.05; OR, 1.21; 95 % CI, 1.03-1.42), with this finding maintained after adjusting for differences in baseline characteristics. AZL-M appeared to have an equivalent safety profile to the ACE-inhibitors, with a similar incidence of adverse events in the two patient groups (p = 0.73).
Conclusions: These data add to the results of previous randomized controlled clinical trials suggesting that, compared with other agents that target the renin-angiotensin system, AZL-M provides statistically significant albeit small improvements in blood pressure control.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

