Reproductive and genital health and risk of cervical human papillomavirus infection: results from the Ludwig-McGill cohort study
- PMID: 26956880
- PMCID: PMC4782350
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-016-1446-x
Reproductive and genital health and risk of cervical human papillomavirus infection: results from the Ludwig-McGill cohort study
Abstract
Background: There are inconsistencies in the literature on reproductive and genital health determinants of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, the primary cause of cervical cancer. We examined these factors in the Ludwig-McGill Cohort Study, a longitudinal, repeated-measurements investigation on the natural history of HPV infection.
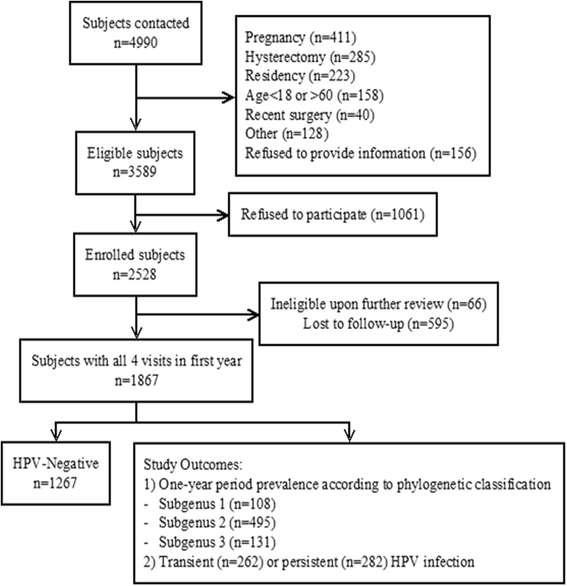
Methods: We analyzed a cohort subset of 1867 women with one complete year of follow-up. We calculated odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for reproductive and genital health characteristics from questionnaire and laboratory data in relation to 1-year period prevalence of HPV infection. Two outcomes were measured; the first based on phylogenetic grouping of HPV types based on tissue tropism and oncogenicity (Alphapapillomavirus Subgenus 1: species 1, 8, 10 and 13; Subgenus 2: species 5, 6, 7, 9, 11; Subgenus 3: species 3, 4 and 14) and the second based on transient or persistent HPV infections.
Results: Lifetime (Subgenus 3 OR = 2.00, CI: 1.23-3.24) and current (Subgenus 3 OR =2.00, CI: 1.15-3.47) condom use and use of contraceptive injections (Subgenus 1 OR = 1.96, CI: 1.22-3.16, Subgenus 2 OR = 1.34, CI: 1.00-1.79) were associated with increased risk of HPV infection. Intrauterine device use was protective (Subgenus 1 OR = 0.48, CI: 0.30-0.75, Subgenus 2 OR = 0.78, CI: 0.62-0.98). These factors were not associated with persistence of HPV infection. Tampon use, previous gynecologic infections and cervical inflammation were associated with an overall increased risk of HPV infection.
Conclusions: Cervical HPV infection was associated with reproductive and genital health factors. Further studies are necessary to confirm the low to moderate associations observed.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin H, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin D. GLOBOCAN 2008 v2.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 10. 2010.
-
- Burchell AN, Winer RL, de Sanjosé S, Franco EL. Chapter 6: Epidemiology and transmission dynamics of genital HPV infection. Vaccine. 2006;24(Suppl 3):S3/52–61. - PubMed
-
- Trottier H, Franco EL. The epidemiology of genital human papillomavirus infection. Vaccine. 2006;24(Suppl 1):S1–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

