Tetherin/BST-2: Restriction Factor or Immunomodulator?
- PMID: 26957198
- PMCID: PMC5466165
- DOI: 10.2174/1570162x14999160224102752
Tetherin/BST-2: Restriction Factor or Immunomodulator?
Abstract
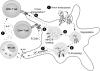
Background: Cell-mediated immune (CMI) responses are critical for the control of HIV-1 infection and their importance was highlighted by the existence of viral proteins, particularly Vpu and Nef, that antagonize these responses. Pandemic HIV-1 Vpu counteracts Tetherin/BST-2, a host factor that could prevent the release of HIV-1 virions by tethering virions on the cell surface, but a link between Tetherin and HIV-1 CMI responses has not yet been demonstrated in vivo. In vitro, the virological and immunological impact of Tetherin-mediated accumulation of virions ranged from enhanced or diminished cell-to-cell spread to enhanced recognition by virus-specific antibodies for natural killer cellmediated lysis. However, Tetherin-restricted virions could be internalized through an endocytosis motif in the Tetherin cytoplasmic tail.
Methods: Given the uncertainties on which in vitro results manifest in vivo and the dearth of knowledge on how Tetherin influences retroviral immunity, in vivo retrovirus infections in mice encoding wild-type, null and endocytosis-defective Tetherin were performed. Here, we review and highlight the results from these in vivo studies.
Results: Current data suggests that endocytosis-defective Tetherin functions as a potent innate restriction factor. By contrast, endocytosis-competent Tetherin, the form found in most mammals including humans and the form counteracted by HIV-1 Vpu, was linked to stronger CMI responses in mice.
Conclusion: We propose that the main role of endocytosis-competent Tetherin is not to directly restrict retroviral replication, but to promote a more effective CMI response against retroviruses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Walker BD, Yu XG. Unravelling the mechanisms of durable control of HIV-1. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13(7):487–498. - PubMed
-
- Ackerman ME, Dugast AS, Alter G. Emerging concepts on the role of innate immunity in the prevention and control of HIV infection. Annual review of medicine. 2012;63:113–130. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz O, Marechal V, Le Gall S, Lemonnier F, Heard JM. Endocytosis of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules is induced by the HIV-1 Nef protein. Nature medicine. 1996;2(3):338–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
