Sonographic Findings of Common Musculoskeletal Diseases in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 26957910
- PMCID: PMC4781764
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2016.17.2.245
Sonographic Findings of Common Musculoskeletal Diseases in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
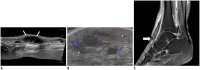
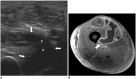
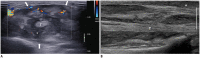
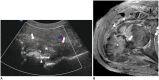
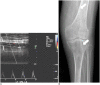
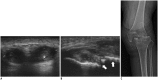
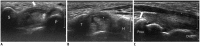
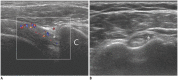
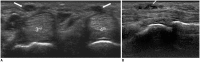
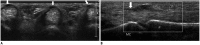
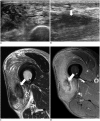
Diabetes mellitus (DM) can accompany many musculoskeletal (MSK) diseases. It is difficult to distinguish the DM-related MSK diseases based on clinical symptoms alone. Sonography is frequently used as a first imaging study for these MSK symptoms and is helpful to differentiate the various DM-related MSK diseases. This pictorial essay focuses on sonographic findings of various MSK diseases that can occur in diabetic patients.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Musculoskeletal; Sonography.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Musculoskeletal infections: ultrasound appearances.Clin Radiol. 2005 Feb;60(2):149-59. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2004.02.005. Clin Radiol. 2005. PMID: 15664569 Review.
-
Rheumatic-musculoskeletal manifestations in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in south India.Int J Rheum Dis. 2011 Feb;14(1):55-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1756-185X.2010.01587.x. Epub 2011 Jan 24. Int J Rheum Dis. 2011. PMID: 21303482
-
Beyond ulcers and osteomyelitis: imaging of less common musculoskeletal complications in diabetes mellitus.Br J Radiol. 2018 Jul;91(1088):20170301. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20170301. Epub 2018 Feb 22. Br J Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29419313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Musculoskeletal manifestations of diabetes mellitus.QJM. 2015 Nov;108(11):853-7. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcv106. Epub 2015 May 28. QJM. 2015. PMID: 26025688 Review.
-
Diabetes mellitus-related musculoskeletal disorders: Unveiling the cluster of diseases.Prim Care Diabetes. 2023 Dec;17(6):548-553. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2023.08.003. Epub 2023 Aug 27. Prim Care Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 37643934 Review.
Cited by
-
Computed Tomography Imaging Characteristics in the Diagnosis and Assessment of Cellulitis in Patients with Leg Swelling.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 May 26;61(6):982. doi: 10.3390/medicina61060982. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40572669 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging for Dupuytren disease: a systematic review of the literature.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019 May 17;20(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s12891-019-2606-0. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019. PMID: 31101038 Free PMC article.
-
The sonographic quantitative assessment of the deltoid muscle to detect type 2 diabetes mellitus: a potential noninvasive and sensitive screening method?BMC Endocr Disord. 2022 Jul 27;22(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s12902-022-01107-2. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022. PMID: 35897066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Joshi N, Caputo GM, Weitekamp MR, Karchmer AW. Infections in patients with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1906–1912. - PubMed
-
- Chau CL, Griffith JF. Musculoskeletal infections: ultrasound appearances. Clin Radiol. 2005;60:149–159. - PubMed
-
- Turecki MB, Taljanovic MS, Stubbs AY, Graham AR, Holden DA, Hunter TB, et al. Imaging of musculoskeletal soft tissue infections. Skeletal Radiol. 2010;39:957–971. - PubMed
-
- Patel SR, Olenginski TP, Perruquet JL, Harrington TM. Pyomyositis: clinical features and predisposing conditions. J Rheumatol. 1997;24:1734–1738. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

