Erratum to: Imprinting disorders: a group of congenital disorders with overlapping patterns of molecular changes affecting imprinted loci
- PMID: 26958095
- PMCID: PMC4782320
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-016-0194-5
Erratum to: Imprinting disorders: a group of congenital disorders with overlapping patterns of molecular changes affecting imprinted loci
Abstract
[This corrects the article DOI: 10.1186/s13148-015-0143-8.].
Figures
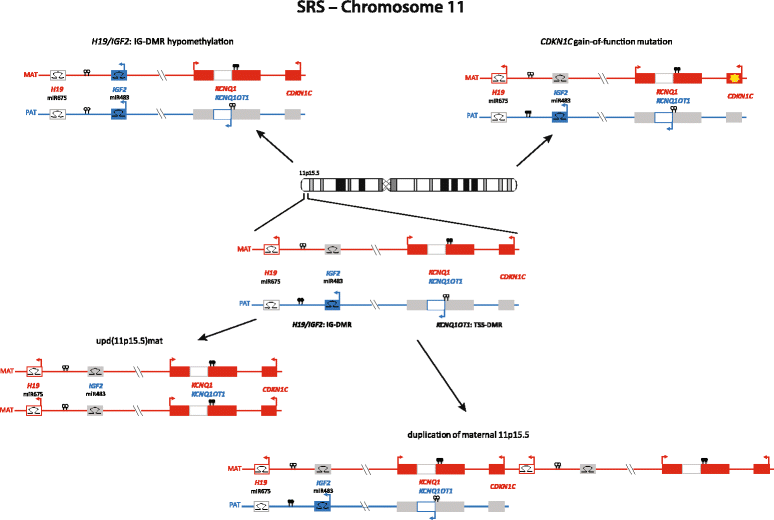
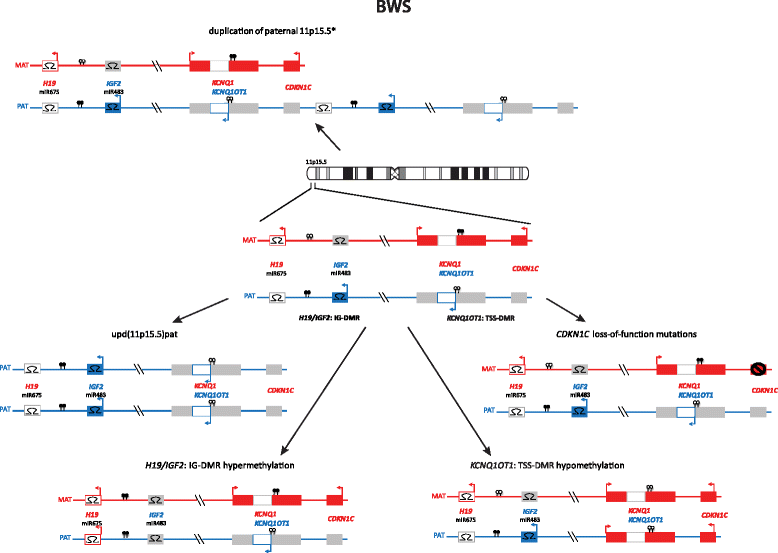
Erratum for
-
Imprinting disorders: a group of congenital disorders with overlapping patterns of molecular changes affecting imprinted loci.Clin Epigenetics. 2015 Nov 14;7:123. doi: 10.1186/s13148-015-0143-8. eCollection 2015. Clin Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 26583054 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Eggermann T, Perez de Nanclares G, Maher ER, Temple IK, Tümer Z, Monk D, Mackay DJ, et al. Imprinting disorders: a group of congenital disorders with overlapping patterns of molecular changes affecting imprinted loci. Clin Epigenetics. 2015;7:123. doi: 10.1186/s13148-015-0143-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

