DNA Aptamers against Taiwan Banded Krait α-Bungarotoxin Recognize Taiwan Cobra Cardiotoxins
- PMID: 26959062
- PMCID: PMC4810211
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins8030066
DNA Aptamers against Taiwan Banded Krait α-Bungarotoxin Recognize Taiwan Cobra Cardiotoxins
Abstract
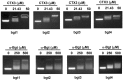
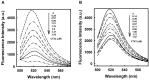
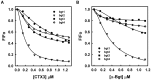
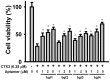
Bungarus multicinctus α-bungarotoxin (α-Bgt) and Naja atra cardiotoxins (CTXs) share a common structural scaffold, and their tertiary structures adopt three-fingered loop motifs. Four DNA aptamers against α-Bgt have been reported previously. Given that the binding of aptamers with targeted proteins depends on structural complementarity, in this study, we investigated whether DNA aptamers against α-Bgt could also recognize CTXs. It was found that N. atra cardiotoxin 3 (CTX3) reduced the electrophoretic mobility of aptamers against α-Bgt. Analysis of the changes in the fluorescence intensity of carboxyfluorescein-labeled aptamers upon binding toxin molecules revealed that CTX3 and α-Bgt could bind the tested aptamers. Moreover, the aptamers inhibited the membrane-damaging activity and cytotoxicity of CTX3. In addition to CTX3, other N. atra CTX isotoxins also bound to the aptamer against α-Bgt. Taken together, our data indicate that aptamers against α-Bgt show cross-reactivity with CTXs. The findings that aptamers against α-Bgt also suppress the biological activities of CTX3 highlight the potential utility of aptamers in regard to the broad inhibition of snake venom three-fingered proteins.
Keywords: aptamer; cardiotoxins; cytotoxicity; membrane-damaging activity; α-bungarotoxin.
Figures

References
-
- Morais V.M., Massaldi H. Snake antivenoms: Adverse reactions and production technology. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2009;15:2–18. doi: 10.1590/S1678-91992009000100002. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

