Metformin Decouples Phospholipid Metabolism in Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 26959405
- PMCID: PMC4784930
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151179
Metformin Decouples Phospholipid Metabolism in Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
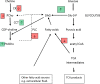
Introduction: The antidiabetic drug metformin, currently undergoing trials for cancer treatment, modulates lipid and glucose metabolism both crucial in phospholipid synthesis. Here the effect of treatment of breast tumour cells with metformin on phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho) metabolism which plays a key role in membrane synthesis and intracellular signalling has been examined.
Methods: MDA-MB-468, BT474 and SKBr3 breast cancer cell lines were treated with metformin and [3H-methyl]choline and [14C(U)]glucose incorporation and lipid accumulation determined in the presence and absence of lipase inhibitors. Activities of choline kinase (CK), CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyl transferase (CCT) and PtdCho-phospholipase C (PLC) were also measured. [3H] Radiolabelled metabolites were determined using thin layer chromatography.
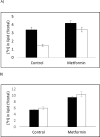
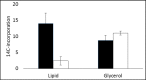
Results: Metformin-treated cells exhibited decreased formation of [3H]phosphocholine but increased accumulation of [3H]choline by PtdCho. CK and PLC activities were decreased and CCT activity increased by metformin-treatment. [14C] incorporation into fatty acids was decreased and into glycerol was increased in breast cancer cells treated with metformin incubated with [14C(U)]glucose.
Conclusion: This is the first study to show that treatment of breast cancer cells with metformin induces profound changes in phospholipid metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Cui Z, Houweling M. Phosphatidylcholine and cell death. Biochim Biophys Acta 2002; 1585(2–3): 87–96. - PubMed
-
- Podo F, Saradanelli F, Iorio E, Canese R, Carpinelli G, Fausto A, et al. Abnormal Choline Phospholipid Metabolism in Breast and Ovary Cancer: Molecular Bases for Noninvasive Imaging Approaches. Current Medical Imaging Reviews 2007; 3(2): 123–137
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

