Perceived exercise barriers are reduced and benefits are improved with lifestyle modification in overweight and obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 26960762
- PMCID: PMC4784413
- DOI: 10.1186/s12905-016-0292-8
Perceived exercise barriers are reduced and benefits are improved with lifestyle modification in overweight and obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: This study assessed the perceived benefits and barriers to exercise participation in overweight and obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and monitored changes in response to a lifestyle intervention.
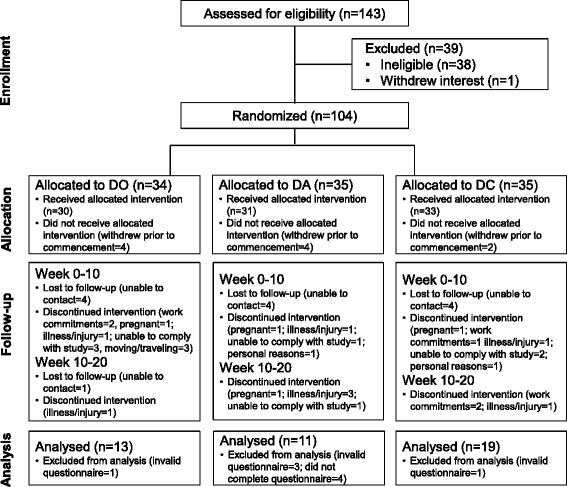
Methods: Forty-three overweight/obese PCOS women (Age, 30.3(6.2) yrs; BMI, 36.4(5.6) kg/m(2)) were randomised to one of three 20-week lifestyle programs: diet only (DO, n = 13), diet and aerobic exercise (DA, n = 11) and diet and combined aerobic-resistance exercise (DC, n = 19). Exercise Benefits/Barriers Scale (EBBS), weight, aerobic fitness, depression and PCOS specific health-related quality of life were measured.
Results: Barriers score was related to depression (r = 0.45, P = 0.002) and aerobic fitness (r = -0.32, P = 0.04), while benefits score was related to aerobic fitness (r = 0.41, P = 0.007). EBBS, benefits and barriers scores improved overtime (P ≤ 0.001). Benefits subscales psychological outlook and social interaction increased (P ≤ 0.001) and life enhancement and preventative health did not change (P ≥ 0.3). Physical performance increased only in DA (P = 0.009). There were no differences between treatments for any of the other subscales (P ≥ 0.2). Barriers subscales exercise milieu, time expenditure and physical exertion reduced (P ≤ 0.003) and family discouragement did not change (P = 0.6).
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that lifestyle modification consisting of an energy-restricted diet with or without exercise training improved the perceived benefits from and barriers to exercise.
Trial registration: Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Register ACTRN12606000198527, registered 26 May 2006.
Figures
References
-
- Wild RA, Carmina E, Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Dokras A, Escobar-Morreale HF, Futterweit W, et al. Assessment of cardiovascular risk and prevention of cardiovascular disease in women with the polycystic ovary syndrome: A Consensus Statement by the Androgen Excess and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (AE-PCOS) Society. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95(5):2038–49. doi: 10.1210/jc.2009-2724. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical