Diet, physical activity, and behavioural interventions for the treatment of overweight or obesity in preschool children up to the age of 6 years
- PMID: 26961576
- PMCID: PMC6669248
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012105
Diet, physical activity, and behavioural interventions for the treatment of overweight or obesity in preschool children up to the age of 6 years
Abstract
Background: Child overweight and obesity has increased globally, and can be associated with short- and long-term health consequences.
Objectives: To assess the effects of diet, physical activity, and behavioural interventions for the treatment of overweight or obesity in preschool children up to the age of 6 years.
Search methods: We performed a systematic literature search in the databases Cochrane Library, MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsycINFO, CINAHL, and LILACS, as well as in the trial registers ClinicalTrials.gov and ICTRP Search Portal. We also checked references of identified trials and systematic reviews. We applied no language restrictions. The date of the last search was March 2015 for all databases.
Selection criteria: We selected randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of diet, physical activity, and behavioural interventions for treating overweight or obesity in preschool children aged 0 to 6 years.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed risk of bias, evaluated the overall quality of the evidence using the GRADE instrument, and extracted data following the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. We contacted trial authors for additional information.
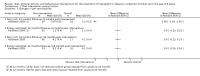
Main results: We included 7 RCTs with a total of 923 participants: 529 randomised to an intervention and 394 to a comparator. The number of participants per trial ranged from 18 to 475. Six trials were parallel RCTs, and one was a cluster RCT. Two trials were three-arm trials, each comparing two interventions with a control group. The interventions and comparators in the trials varied. We categorised the comparisons into two groups: multicomponent interventions and dietary interventions. The overall quality of the evidence was low or very low, and six trials had a high risk of bias on individual 'Risk of bias' criteria. The children in the included trials were followed up for between six months and three years.In trials comparing a multicomponent intervention with usual care, enhanced usual care, or information control, we found a greater reduction in body mass index (BMI) z score in the intervention groups at the end of the intervention (6 to 12 months): mean difference (MD) -0.3 units (95% confidence interval (CI) -0.4 to -0.2); P < 0.00001; 210 participants; 4 trials; low-quality evidence, at 12 to 18 months' follow-up: MD -0.4 units (95% CI -0.6 to -0.2); P = 0.0001; 202 participants; 4 trials; low-quality evidence, and at 2 years' follow-up: MD -0.3 units (95% CI -0.4 to -0.1); 96 participants; 1 trial; low-quality evidence.One trial stated that no adverse events were reported; the other trials did not report on adverse events. Three trials reported health-related quality of life and found improvements in some, but not all, aspects. Other outcomes, such as behaviour change and parent-child relationship, were inconsistently measured.One three-arm trial of very low-quality evidence comparing two types of diet with control found that both the dairy-rich diet (BMI z score change MD -0.1 units (95% CI -0.11 to -0.09); P < 0.0001; 59 participants) and energy-restricted diet (BMI z score change MD -0.1 units (95% CI -0.11 to -0.09); P < 0.0001; 57 participants) resulted in greater reduction in BMI than the comparator at the end of the intervention period, but only the dairy-rich diet maintained this at 36 months' follow-up (BMI z score change in MD -0.7 units (95% CI -0.71 to -0.69); P < 0.0001; 52 participants). The energy-restricted diet had a worse BMI outcome than control at this follow-up (BMI z score change MD 0.1 units (95% CI 0.09 to 0.11); P < 0.0001; 47 participants). There was no substantial difference in mean daily energy expenditure between groups. Health-related quality of life, adverse effects, participant views, and parenting were not measured.No trial reported on all-cause mortality, morbidity, or socioeconomic effects.All results should be interpreted cautiously due to their low quality and heterogeneous interventions and comparators.
Authors' conclusions: Muticomponent interventions appear to be an effective treatment option for overweight or obese preschool children up to the age of 6 years. However, the current evidence is limited, and most trials had a high risk of bias. Most trials did not measure adverse events. We have identified four ongoing trials that we will include in future updates of this review.The role of dietary interventions is more equivocal, with one trial suggesting that dairy interventions may be effective in the longer term, but not energy-restricted diets. This trial also had a high risk of bias.
Conflict of interest statement
JC: none known.
EL: none known.
COM: none known.
LA: none known.
EM: none known.
LAl‐K: none known.
LE: none known.
MIM: none known.
KR: none known.
Figures













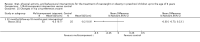


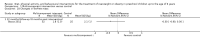











References
References to studies included in this review
Bocca 2012 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Bocca G, Corpeleijn E, Stolk RP, Sauer PJ. Results of a multidisciplinary treatment program in 3‐year‐old to 5‐year‐old overweight or obese children: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2012;166(12):1109‐15. - PubMed
-
- Bocca G, Corpeleijn E, Heuvel ER, Stolk RP, Sauer PJ. Three‐year follow‐up of 3‐year‐old to 5‐year‐old children after participation in a multidisciplinary or a usual‐care obesity treatment program. Clin Nutr 2014;33(6):1095‐100. - PubMed
-
- Bocca G, Kuitert MW, Sauer PJ, Stolk RP, Flapper BC, Corpeleijn E. A multidisciplinary intervention programme has positive effects on quality of life in overweight and obese preschool children. Acta Paediatr 2014;103(9):962‐7. - PubMed
-
- Bocca G, Stolk R, Sauer P. Long lasting positive effects of a multidisciplinary intervention program to treat obesity in preschool children. Hormone Research in Paediatrics 2011;76:181.
-
- NTR872. The effectiveness of multidisciplinary treatment in young overweight: GECKO Outpatients Clinic, a randomized controlled trial. http://www.trialregister.nl/trialreg/admin/rctview.asp?TC=872 (accessed 11 November 2015).
Kelishadi 2009 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Kelishadi R, Zemel MB, Hashemipour M, Hosseini M, Mohammadifard N, Poursafa P. Can a dairy‐rich diet be effective in long‐term weight control of young children?. J Am Coll Nutr 2009;28(5):601‐10. - PubMed
Lanigan 2010 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Lanigan J, Collins S, Birbara T, Kokoreli M, Singhal A. The TrimTots programme for prevention and treatment of obesity in preschool children: evidence from two randomised controlled trials. The Lancet 2013;382(Supplement 3):S58.
-
- Lanigan JA, Low SL, Lanigan‐Coyte KM, Tang HA, Birbara T, Kokoreli M, et al. Prevention of obesity in preschool children. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2010;18:S104.
-
- NCT00675662. TrimTots pre‐school obesity prevention programme. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00675662 (accessed 11 November 2015).
Quattrin 2012 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- NCT01029834. Treating overweight youth: a family based approach in primary care. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01029834 (accessed 11 November 2015).
Stark 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- NCT01018121. LAUNCH II: Learning about activity and understanding nutrition for better child health. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01018121 (accessed 11 November 2015).
Stark 2014 {published and unpublished data}
-
- NCT01419951. Launch II: A pilot randomized control trial of a clinic and clinic plus home intervention for preschool obesity. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01419951 (accessed 11 November 2015).
Taveras 2011 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- NCT00377767. Improving primary care to prevent childhood obesity. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00377767 (accessed 11 November 2015).
References to studies excluded from this review
Berner 2015 {published data only}
-
- Berner N, Jay M, Lewis K, Hung W, Squires A, Ngai G. Comparison of parent and child versus child‐only weight management interventions in the patient‐centered medical home. Journal of Clinical Outcomes Management 2015;22(2):57‐60.
ChiCTR‐TRC‐12001880 {published data only}
-
- A novel intervention to modify dietary behaviors related to childhood obesity based on behavior modification theory: a cluster randomized controlled trial. http://www.chictr.org/en/proj/show.aspx?proj=2391.
NCT00528164 {published data only}
-
- NCT00528164. Team PLAY (positive lifestyles for active youngsters). http://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT00528164. - PMC - PubMed
NCT01515254 {published data only}
-
- NCT01515254. The feeding dynamic intervention: self regulation of intake in preschoolers (FeeDIn). http://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT01515254.
NCT01546727 {published data only}
-
- NCT01546727. Behavioral treatment for obese preschoolers. http://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT01546727.
NCT01552642 {published data only}
-
- NCT01552642. An interactive web‐based intervention to achieve healthy weight in young children. http://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT01552642. - PMC - PubMed
NCT01610219 {published data only}
-
- NCT01610219. Lifestyle modification for type 2 diabetes prevention in overweight youth. http://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT01610219.
NCT01792531 {published data only}
-
- NCT01792531. The More & Less Study: A trial testing different treatment approaches to obesity in preschoolers. http://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT01792531.
NCT02373670 {published data only}
-
- NCT02373670. Parent mentors using positive deviance in childhood obesity. http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02373670.
Resnicow 2012 {published data only}
Van Allen 2014 {published data only}
References to ongoing studies
NCT00916318 {published data only}
-
- Önnerfält J, Erlandsson L‐K, Orban K, Broberg M, Helgason C, Thorngren‐Jerneck K. A family‐based intervention targeting parents of preschool children with overweight and obesity: conceptual framework and study design of LOOPS ‐ Lund overweight and obesity preschool study. BMC Public Health 2012;12:879. - PMC - PubMed
NCT01698606 {published data only}
-
- Block, D. FOR HEALTH: A family‐oriented healthy eating, activity and lifestyle training with hands‐on experience for overweight and obese preschool children and their families ‐ a pilot trial. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01698606 (accessed 11 November 2015).
NCT02292602 {published data only}
-
- Kuhl, E. Developing a preschool obesity intervention for families enrolled in WIC. http://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT02292602 (accessed 11 November 2015).
Reifsnider 2012 {published data only}
-
- Reifsnider EA, Militello L. Reducing childhood obesity among WIC recipients. Communicating nursing research 2012;45:442.
Additional references
Baxter 2015
Beller 2013
Bluford 2007
-
- Bluford DAA, Sherry B, Scanlon KS. Interventions to prevent or treat obesity in preschool children: A review of evaluated programs. Obesity 2007;15:1356‐72. - PubMed
Bocca 2013
-
- Bocca G, Ongering EC, Stolk RP, Sauer PJ. Insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk factors in 3‐ to 5‐year old overweight or obese children. Hormone Research in Paediatrics 2013;80(3):201–6. - PubMed
Bond 2009
-
- Bond M, Wyatt K, Lloyd J, Welch K, Taylor R. Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost‐effectiveness of weight management schemes for the under fives: a short report. Health Technol Assess 2009;13:1‐75, iii. - PubMed
Bond 2011
-
- Bond M, Wyatt K, Lloyd J, Taylor R. Systematic review of the effectiveness of weight management schemes for the under fives. Obesity Reviews 2011;12:242‐53. - PubMed
Cataldo 2015
Clark 2007
-
- Clark HR, Goyder E, Bissell P, Blank L, Peters J. How do parents’ child feeding behaviours influence child weight? Implications for childhood obesity policy. Journal of Public Health 2007;29:132‐41. - PubMed
CMO 2015
-
- Chief Medical Officer. Annual Report of the Chief Medical Officer: Surveillance Volume, 2012: On the State of the Public’s Health. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/chief‐medical‐officer‐annualr... (accessed 30 March 2015).
Cole 2000
Cole 2012
-
- Cole TJ, Lobstein T. Extended international (IOTF) body mass index cut‐offs for thinness, overweight and obesity. Pediatric Obesity 2012;7(4):284–94. - PubMed
Daniels 2009
-
- Daniels SR. Complications of obesity in children and adolescents. International Journal of Obesity 2009;33(Suppl 1):S60–5. - PubMed
de Onis 2010
-
- Onis M, Blössner M, Borghi E. Global prevalence and trends of overweight and obesity among preschool children. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2010;92(5):1257‐64. - PubMed
Eady 2008
Egan 2013
Egbewale 2014
Ells 2015
Follmann 1992
-
- Follmann D, Elliot P, Suh I, Cutler J. Variance imputation for overviews of clinical trials with continuous response. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1992;45(7):769‐73. - PubMed
Ford 2010
-
- Ford AL, Hunt LP, Cooper A, Shield JPH. What reduction in BMI SDS is required in obese adolescents to improve body composition and cardiometabolic health?. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2010;95:256–61. - PubMed
Freedman 2006
-
- Freedman DS, Khan LK, Serdula MK, Ogden CL, Dietz WH. Racial and ethnic differences in secular trends for childhood BMI, weight, and height. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2006;14(2):301‐8. - PubMed
Glenny 1997
-
- Glenny AM, O'Meara S, Melville A, Sheldon TA, Wilson C. The treatment and prevention of obesity: a systematic review of the literature. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders 1997;21(9):715‐37. - PubMed
Golan 2004
-
- Golan M, Crow S. Targeting parents exclusively in the treatment of childhood obesity: long‐term results. Obesity Research 2004;12:357‐61. - PubMed
Griffiths 2010
-
- Griffiths LJ, Parsons TJ, Hill AJ. Self‐esteem and quality of life in obese children and adolescents: a systematic review. International Journal of Pediatric Obesity 2010;5(4):282–304. - PubMed
Gustafson 2006
-
- Gustafson SL, Rhodes RE. Parental correlates of physical activity in children and early adolescents. Sports Medicine 2006;36:79‐97. - PubMed
Halliday 2014
-
- Halliday JA, Palma CL, Mellor D, Green J, Renzaho AMN. The relationship between family functioning and child and adolescent overweight and obesity: a systematic review. International Journal of Obesity 2014;38:480‐93. - PubMed
Higgins 2002
-
- Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21(11):1539‐58. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2009
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011b
Hróbjartsson 2013
-
- Hróbjartsson A, Thomsen AS, Emanuelsson F, Tendal B, Hilden J, Boutron I, et al. Observer bias in randomized clinical trials with measurement scale outcomes: a systematic review of trials with both blinded and nonblinded assessors. Canadian Medical Association Journal 2013;185(4):E201‐11. - PMC - PubMed
HSCIC 2015
-
- Health and Social Care Information Centre. National Child Measurement Programme ‐ England, 2012‐13 school year. http://www.hscic.gov.uk/article/2021/Website‐Search?productid=13778&... (accessed 30 March 2015).
Kelly 2013
-
- Kelly AS, Barlow SE, Rao G, Inge TH, Hayman LL, Steinberger J, et al. Severe obesity in children and adolescents: identification, associated health risks, and treatment approaches: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2013;128(15):1689–712. - PubMed
Kirkham 2010
Knai 2012
Leclercq 2013
-
- Leclercq E, Leeflang MM, Dalen EC, Kremer LC. Validation of search filters for identifying pediatric studies in PubMed. The Journal of Pediatrics 2013;162(3):629‐34. - PubMed
Liberati 2009
Lobstein 2004
-
- Lobstein T, Baur L, Uauy R. Obesity in children and young people: a crisis in public health. Obesity Reviews 2004;5(Suppl 1):4‐104. - PubMed
Meader 2014
Narang 2012
NCB 2015
-
- National Children's Bureau. Poor beginnings. Health inequalities among young children across England. A National Children's Bureau Report 2015.
Ng 2014
NOO NHS 2011
-
- National Obesity Observatory on behalf of the Public Health Observatories in England. A simple guide to classifying body mass index in children, 2011. www.noo.org.uk/uploads/doc/vid_11601_A_simple_guide_to_classifying_BMI_i... (accessed 3 November 2015).
Ogden 2006
-
- Ogden J, Reynolds R, Smith A. Expanding the concept of parental control: A role for overt and covert control in children’s snacking behaviour?. Appetite 2006;47:100‐6. - PubMed
Olds 2011
-
- Olds T, Maher C, Zumin S, Péneau S, Lioret S, CastetbonK, et al. Evidence that the prevalence of childhood overweight is plateauing: data from nine countries. International Journal of Pediatric Obesity 2011;6(5‐6):342–60. - PubMed
Paes 2015
Parsons 1999
-
- Parsons TJ, Power C, Logan S, Summerbell CD. Childhood predictors of adult obesity: a systematic review. International Journal of Obesity 1999;23(Suppl 8):S1–S107. - PubMed
Paulis 2014
-
- Paulis WD, Silva S, Koes BW, Middelkoop M. Overweight and obesity are associated with musculoskeletal complaints as early as childhood: a systematic review. Obesity Reviews 2014;15(1):52–67. - PubMed
Puhl 2007
-
- Puhl RM, Latner JD. Stigma, obesity, and the health of the nation’s children. Psychology Bulletin 2007;133(4):557‐80. - PubMed
Rajput 2014
-
- Rajput N, Tuohy P, Mishra S, Smith A, Taylor B. Overweight and obesity in 4‐5‐year‐old children in New Zealand: Results from the first 4 years (2009‐2012) of the B4School Check programme. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health 2014;51(3):334–43. - PubMed
Reilly 2003
Reilly 2011
-
- Reilly JJ, Kelly J. Long‐term impact of overweight and obesity in childhood and adolescence on morbidity and premature mortality in adulthood: systematic review. International Journal of Obesity 2011;35(7):891–8. - PubMed
Riley 2011
-
- Riley RD, Higgins JP, Deeks JJ. Interpretation of random effects meta‐analyses. BMJ 2011;342:d549. - PubMed
Rokholm 2010
-
- Rokholm B, Baker JL, Sørenson TI. The levelling off of the obesity epidemic since the year 1999 ‐ a review of evidence and perspectives. Obesity Reviews 2010;11(12):835–46. - PubMed
Shrewsbury 2008
-
- Shrewsbury V, Wardle J. Socioeconomic status and adiposity in childhood: a systematic review of cross‐sectional studies 1990‐2005. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008;16(2):275‐84. - PubMed
Singh 2008
-
- Singh AS, Mulder C, Twisk JW, Mechelen W, Chinapaw MJ. Tracking of childhood overweight into adulthood: a systematic review of the literature. Obesity Reviews 2008;9(5):474–88. - PubMed
Skinner 2014
-
- Skinner AC, Skelton JA. Prevalence and trends in obesity and severe obesity among children in the United States, 1999‐2012. JAMA Pediatrics 2014;168(6):561‐6. - PubMed
Sleddens 2011
-
- Sleddens EF, Gerards SM, Thijs C, Vries NK, Kremers SP. General parenting, childhood overweight and obesity‐inducing behaviors: a review. International Journal of Pediatric Obesity 2011;6:e12‐27. - PubMed
Sterne 2011
-
- Sterne JA, Sutton AJ, Ioannidis JP, Terrin N, Jones DR, Lau J, et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta‐analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2011;343:d4002. - PubMed
Tang‐Peronard 2008
-
- Tang‐Peronard JL, Heitmann BL. Stigmatization of obese children and adolescents, the importance of gender. Obesity Reviews 2008;9(6):522–34. - PubMed
Wang 2012
Wansink 2006
-
- Wansink B. Nutritional gatekeepers and the 72% solution. Journal of the American Dietetic Association 2006;106:1324‐7. - PubMed
Whitaker 1997
-
- Whitaker RC, Wright JA, Pepe MS, Seidel KD, Dietz WH. Predicting obesity in young adulthood from childhood and parental obesity. The New England Journal of Medicine 1997;337(13):869–73. - PubMed
WHO 2015a
-
- World Health Organization. Fact sheet on overweight and obesity. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en (accessed 30 March 2015).
WHO 2015b
-
- World Health Organization. The WHO Child Growth Standards. http://www.who.int/childgrowth/publications/technical˙report˙pub/en/ (accessed 30 March 2015).
Wong 2006a
Wong 2006b
-
- Wong SS, Wilczynski NL, Haynes RB. Optimal CINAHL search strategies for identifying therapy studies and review articles. Journal of Nursing Scholarship 2006;38(2):194‐9. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Oude Luttikhuis 2009
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

