Discovery of high affinity inhibitors of Leishmania donovani N-myristoyltransferase
- PMID: 26962429
- PMCID: PMC4757855
- DOI: 10.1039/c5md00241a
Discovery of high affinity inhibitors of Leishmania donovani N-myristoyltransferase
Abstract
N-Myristoyltransferase (NMT) is a potential drug target in Leishmania parasites. Scaffold-hopping from published inhibitors yielded the serendipitous discovery of a chemotype selective for Leishmania donovani NMT; development led to high affinity inhibitors with excellent ligand efficiency. The binding mode was characterised by crystallography and provides a structural rationale for selectivity.
Figures

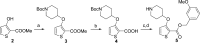




References
-
- Pearson R. D., de Queiroz Sousa A. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996;22:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Desjeux P. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2004;27:305–318. - PubMed
-
- Chappuis F., Sundar S., Hailu A., Ghalib H., Rijal S., Peeling R. W., Alvar J., Boelaert M. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007;5:873–882. - PubMed
-
- WHO Leishmaniasis Programme, http://www.who.int/leishmaniasis/en/itle, 2010.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

