GIS-NaP1 zeolite microspheres as potential water adsorption material: Influence of initial silica concentration on adsorptive and physical/topological properties
- PMID: 26964638
- PMCID: PMC4786819
- DOI: 10.1038/srep22734
GIS-NaP1 zeolite microspheres as potential water adsorption material: Influence of initial silica concentration on adsorptive and physical/topological properties
Abstract
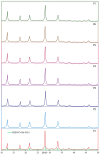
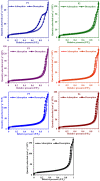
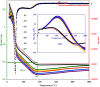
GIS-NaP1 zeolite samples were synthesized using seven different Si/Al ratios (5-11) of the hydrothermal reaction mixtures having chemical composition Al2O3:xSiO2:14Na2O:840H2O to study the impact of Si/Al molar ratio on the water vapour adsorption potential, phase purity, morphology and crystal size of as-synthesized GIS-NaP1 zeolite crystals. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) observations reveal that Si/Al ratio does not affect the phase purity of GIS-NaP1 zeolite samples as high purity GIS-NaP1 zeolite crystals were obtained from all Si/Al ratios. Contrary, Si/Al ratios have remarkable effect on the morphology, crystal size and porosity of GIS-NaP1 zeolite microspheres. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) evaluations of individual GIS-NaP1 zeolite microsphere demonstrate the characteristic changes in the packaging/arrangement, shape and size of primary nano crystallites. Textural characterisation using water vapour adsorption/desorption, and nitrogen adsorption/desorption data of as-synthesized GIS-NaP1 zeolite predicts the existence of mix-pores i.e., microporous as well as mesoporous character. High water storage capacity 1727.5 cm(3) g(-1) (138.9 wt.%) has been found for as-synthesized GIS-NaP1 zeolite microsphere samples during water vapour adsorption studies. Further, the total water adsorption capacity values for P6 (1299.4 mg g(-1)) and P7 (1388.8 mg g(-1)) samples reveal that these two particular samples can absorb even more water than their own weights.
Figures














References
-
- Sharma P., Yeo J.-G., Han M. H. & Cho C. H. Knobby surfaced, mesoporous, single-phase GIS-NaP1 zeolite microsphere synthesis and characterization for H2 gas adsorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 2602–2612 (2013).
-
- Henninger S. K., Schmidt F. P. & Henning H.-M. Water adsorption characteristics of novel materials for heat transformation applications. Appl. Thermal Eng. 30, 1692–1702 (2010).
-
- Jänchen J., Ackermann D., Stach H. & Brösicke W. Studies of the water adsorption on Zeolites and modified mesoporous materials for seasonal storage of solar heat. Solar Energy 76, 339–344 (2004).
-
- Ng K. C. Recent developments in heat-driven silica gel-water adsorption chillers. Heat Transfer Eng. 24, 1–3 (2003).
-
- Ng E.-P. & Mintova S. Nanoporous materials with enhanced hydrophilicity and high water sorption capacity. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 114, 1–26 (2008).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

