Pancreatic regulation of glucose homeostasis
- PMID: 26964835
- PMCID: PMC4892884
- DOI: 10.1038/emm.2016.6
Pancreatic regulation of glucose homeostasis
Abstract
In order to ensure normal body function, the human body is dependent on a tight control of its blood glucose levels. This is accomplished by a highly sophisticated network of various hormones and neuropeptides released mainly from the brain, pancreas, liver, intestine as well as adipose and muscle tissue. Within this network, the pancreas represents a key player by secreting the blood sugar-lowering hormone insulin and its opponent glucagon. However, disturbances in the interplay of the hormones and peptides involved may lead to metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) whose prevalence, comorbidities and medical costs take on a dramatic scale. Therefore, it is of utmost importance to uncover and understand the mechanisms underlying the various interactions to improve existing anti-diabetic therapies and drugs on the one hand and to develop new therapeutic approaches on the other. This review summarizes the interplay of the pancreas with various other organs and tissues that maintain glucose homeostasis. Furthermore, anti-diabetic drugs and their impact on signaling pathways underlying the network will be discussed.
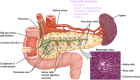
Figures



References
-
- Brissova M, Fowler MJ, Nicholson WE, Chu A, Hirshberg B, Harlan DM et al. Assessment of human pancreatic islet architecture and composition by laser scanning confocal microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem 2005; 53: 1087–1097. - PubMed
-
- Katsuura G, Asakawa A, Inui A. Roles of pancreatic polypeptide in regulation of food intake. Peptides 2002; 23: 323–329. - PubMed
-
- Wierup N, Svensson H, Mulder H, Sundler F. The ghrelin cell: a novel developmentally regulated islet cell in the human pancreas. Regul Pept 2002; 107: 63–69. - PubMed
-
- Goke B. Islet cell function: alpha and beta cells—partners towards normoglycaemia. Int J Clin Pract Suppl 2008; 159: 2–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

