Role of docosahexaenoic acid in the modulation of glial cells in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 26965310
- PMCID: PMC4787218
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-016-0525-7
Role of docosahexaenoic acid in the modulation of glial cells in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
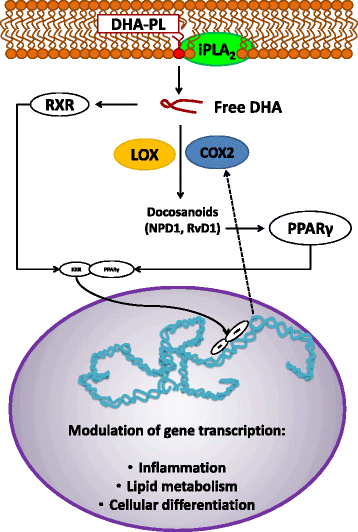
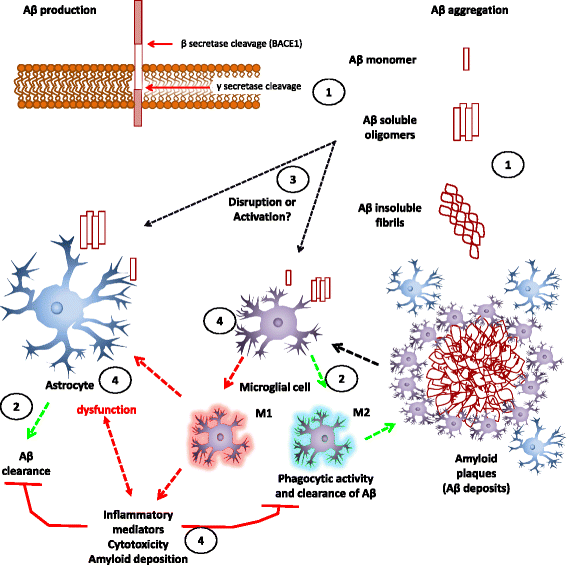
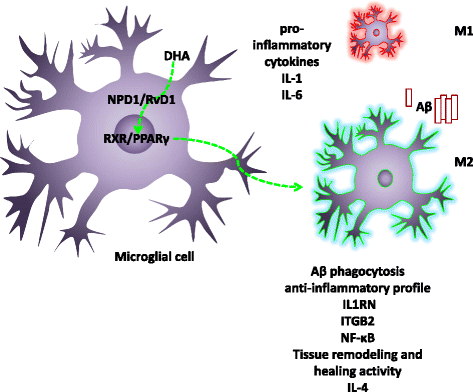
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is an omega-3 (ω-3) long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid (LCPUFA) relevant for brain function. It has largely been explored as a potential candidate to treat Alzheimer's disease (AD). Clinical evidence favors a role for DHA in the improvement of cognition in very early stages of the AD. In response to stress or damage, DHA generates oxygenated derivatives called docosanoids that can activate the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ). In conjunction with activated retinoid X receptors (RXR), PPARγ modulates inflammation, cell survival, and lipid metabolism. As an early event in AD, inflammation is associated with an excess of amyloid β peptide (Aβ) that contributes to neural insult. Glial cells are recognized to be actively involved during AD, and their dysfunction is associated with the early appearance of this pathology. These cells give support to neurons, remove amyloid β peptides from the brain, and modulate inflammation. Since DHA can modulate glial cell activity, the present work reviews the evidence about this modulation as well as the effect of docosanoids on neuroinflammation and in some AD models. The evidence supports PPARγ as a preferred target for gene modulation. The effective use of DHA and/or its derivatives in a subgroup of people at risk of developing AD is discussed.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease (AD); Amyloid β peptide (Aβ); Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA); Glial cells; Neuroinflammation; Neuroprotectin D1 (NPD1); Resolvin D1 (RvD1).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Docosahexaenoic acid-derived neuroprotectin D1 induces neuronal survival via secretase- and PPARγ-mediated mechanisms in Alzheimer's disease models.PLoS One. 2011 Jan 5;6(1):e15816. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015816. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21246057 Free PMC article.
-
Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LCPUFA) from genesis to senescence: the influence of LCPUFA on neural development, aging, and neurodegeneration.Prog Lipid Res. 2014 Jan;53:1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.10.002. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Prog Lipid Res. 2014. PMID: 24334113 Review.
-
Oxidized Docosahexaenoic Acid Species and Lipid Peroxidation Products Increase Amyloidogenic Amyloid Precursor Protein Processing.Neurodegener Dis. 2016;16(1-2):44-54. doi: 10.1159/000440839. Neurodegener Dis. 2016. PMID: 26642316
-
Docosanoids and elovanoids from omega-3 fatty acids are pro-homeostatic modulators of inflammatory responses, cell damage and neuroprotection.Mol Aspects Med. 2018 Dec;64:18-33. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2018.09.003. Epub 2018 Oct 1. Mol Aspects Med. 2018. PMID: 30244005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membrane lipid modifications and therapeutic effects mediated by hydroxydocosahexaenoic acid on Alzheimer's disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jun;1838(6):1680-92. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.12.016. Epub 2013 Dec 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24374316
Cited by
-
Effects of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Brain Functions: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2022 Oct 9;14(10):e30091. doi: 10.7759/cureus.30091. eCollection 2022 Oct. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36381743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ω-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Improve the Blood-Brain-Barrier Integrity in Contrast-Induced Blood-Brain-Barrier Injury in Uremic Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 29;24(15):12168. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512168. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569545 Free PMC article.
-
Omega-3 Fatty Acid-Type Docosahexaenoic Acid Protects against Aβ-Mediated Mitochondrial Deficits and Pathomechanisms in Alzheimer's Disease-Related Animal Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 29;21(11):3879. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113879. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32486013 Free PMC article.
-
Amelioration of Cognitive and Olfactory System Deficits in APOE4 Transgenic Mice with DHA Treatment.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Oct;60(10):5624-5641. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03401-z. Epub 2023 Jun 17. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37329383
-
Modulation of innate immunity of patients with Alzheimer's disease by omega-3 fatty acids.FASEB J. 2017 Aug;31(8):3229-3239. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700065R. Epub 2017 Apr 18. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28420693 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

