Potential impact of the implementation of multiple-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) on the Polish pricing and reimbursement process of orphan drugs
- PMID: 26965710
- PMCID: PMC4787054
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-016-0388-0
Potential impact of the implementation of multiple-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) on the Polish pricing and reimbursement process of orphan drugs
Abstract
Background: The objective of this study was to assess the potential impact of the implementation of multiple-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) on the Polish pricing and reimbursement (P&R) process with regard to orphan drugs.
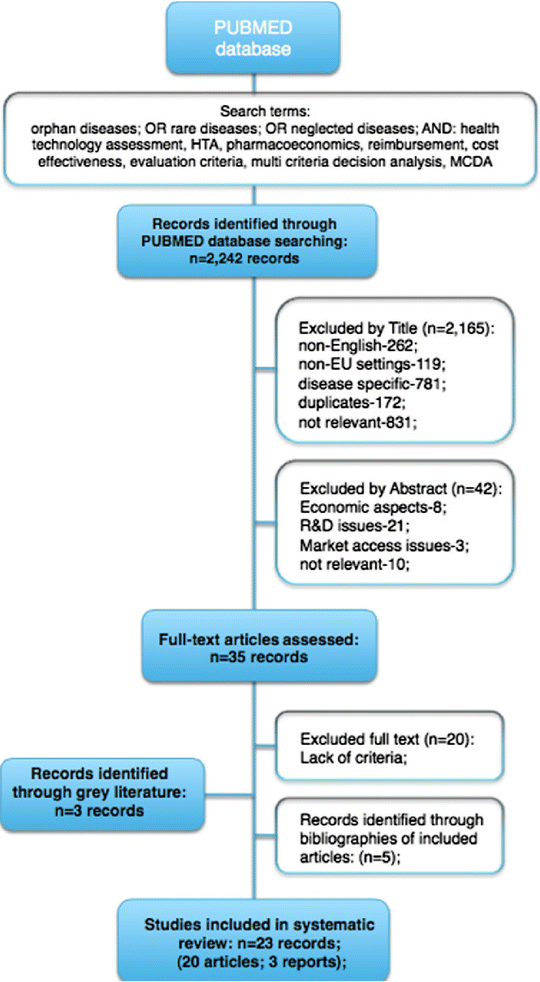
Methods: A four step approach was designed. Firstly, a systematic literature review was conducted to select the MCDA criteria. Secondly, a database of orphan drugs was established. Thirdly, health technology appraisals (HTA recommendations) were categorized and an MCDA appraisal was conducted. Finally, a comparison of HTA and MCDA outcomes was carried out. An MCDA outcome was considered positive if more than 50% of the maximum number of points was reached (base case). In the sensitivity analysis, 25% and 75% thresholds were tested as well.
Results: Out of 2242 publications, 23 full-text articles were included. The final MCDA tool consisted of ten criteria. In total, 27 distinctive drug-indication pairs regarding 21 drugs were used for the study. Six negative and 21 positive HTA recommendations were issued. In the base case, there were 19 positive MCDA outcomes. Of the 27 cases, there were 12 disagreements between the HTA and MCDA outcomes, the majority of which related to positive HTA guidance for negative MCDA outcomes. All drug-indication pairs with negative HTA recommendations were appraised positively in the MCDA framework. Economic details were available for 12 cases, of which there were 9 positive MCDA outcomes. Amongst the 12 drug-indication pairs, two were negatively appraised in the HTA process, with positive MCDA guidance, and two were appraised in the opposite direction.
Conclusions: An MCDA approach may lead to different P&R outcomes compared to a standard HTA process. On the one hand, enrichment of the list of decision making criteria means further scrutiny of a given health technology and as such increases the odds of a negative P&R outcome. On the other hand, it may uncover additional values and as such increase the odds of positive P&R outcomes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Revealed preferences towards the appraisal of orphan drugs in Poland - multi criteria decision analysis.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2018 Apr 27;13(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s13023-018-0803-9. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2018. PMID: 29703227 Free PMC article.
-
Multicriteria decision analysis (MCDA) for health technology assessment: the Queensland Health experience.Aust Health Rev. 2019 Oct;43(5):591-599. doi: 10.1071/AH18042. Aust Health Rev. 2019. PMID: 30205873
-
International experiences in multicriteria decision analysis (MCDA) for evaluating orphan drugs: a scoping review.Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2019 Aug;19(4):409-420. doi: 10.1080/14737167.2019.1633918. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2019. PMID: 31210065
-
Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) Models in Health Technology Assessment of Orphan Drugs-a Systematic Literature Review. Next Steps in Methodology Development?Front Public Health. 2018 Oct 15;6:287. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2018.00287. eCollection 2018. Front Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30374435 Free PMC article.
-
Multicriteria Decision Analysis to Support Health Technology Assessment Agencies: Benefits, Limitations, and the Way Forward.Value Health. 2019 Nov;22(11):1283-1288. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2019.06.014. Epub 2019 Oct 16. Value Health. 2019. PMID: 31708065
Cited by
-
What attributes should be included in a discrete choice experiment related to health technologies? A systematic literature review.PLoS One. 2019 Jul 18;14(7):e0219905. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0219905. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31318926 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of criteria and COVID-19 patients for intensive care unit admission in the era of pandemic: A multi-criteria decision making approach.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021 Sep;209:106348. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106348. Epub 2021 Aug 8. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021. PMID: 34391998 Free PMC article.
-
Development of the Emirates Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis Tool for Orphan Drugs.Cureus. 2024 Feb 29;16(2):e55215. doi: 10.7759/cureus.55215. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38558740 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapy with alglucosidase alfa in adult patients with Pompe disease.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017 Dec 13;12(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s13023-017-0731-0. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017. PMID: 29237491 Free PMC article.
-
Using Genomic Information to Guide Ibrutinib Treatment Decisions in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis.Pharmacoeconomics. 2017 Aug;35(8):845-858. doi: 10.1007/s40273-017-0519-z. Pharmacoeconomics. 2017. PMID: 28762015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- EUnetHTA. http://www.eunethta.eu/faq/Category%201-0#t287n73. Accessed November 2015.
-
- Culyer T. Where are the Limits of Cost-Effectiveness Analysis and Health Technology Assessment? J Med Assoc Thai. 2014;97(Suppl. 5):S1–S2. - PubMed
-
- Devlin NJ, Sussex J. Incorporating multiple criteria in HTA, methods and processes. Office of Health Economics. 2011; 1–60. ISBN: 978-1-899040-98-8. https://www.ohe.org/publications/incorporating-multiple-criteria-hta-met.... Access 6 March 2016.
-
- Figueira J, Greco S, Ehrgott M. Series: International Series in Operations Research & Management Science, Vol. 78. New York, USA: Springer Science + Business Media; 2005. Multiple criteria decision analysis: state of the art surveys.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

