Post-Inhibitory Rebound Spikes in Rat Medial Entorhinal Layer II/III Principal Cells: In Vivo, In Vitro, and Computational Modeling Characterization
- PMID: 26965902
- PMCID: PMC5963826
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhw058
Post-Inhibitory Rebound Spikes in Rat Medial Entorhinal Layer II/III Principal Cells: In Vivo, In Vitro, and Computational Modeling Characterization
Abstract
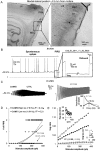
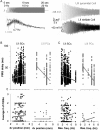
Medial entorhinal cortex Layer-II stellate cells (mEC-LII-SCs) primarily interact via inhibitory interneurons. This suggests the presence of alternative mechanisms other than excitatory synaptic inputs for triggering action potentials (APs) in stellate cells during spatial navigation. Our intracellular recordings show that the hyperpolarization-activated cation current (Ih) allows post-inhibitory-rebound spikes (PIRS) in mEC-LII-SCs. In vivo, strong inhibitory-post-synaptic potentials immediately preceded most APs shortening their delay and enhancing excitability. In vitro experiments showed that inhibition initiated spikes more effectively than excitation and that more dorsal mEC-LII-SCs produced faster and more synchronous spikes. In contrast, PIRS in Layer-II/III pyramidal cells were harder to evoke, voltage-independent, and slower in dorsal mEC. In computational simulations, mEC-LII-SCs morphology and Ih homeostatically regulated the dorso-ventral differences in PIRS timing and most dendrites generated PIRS with a narrow range of stimulus amplitudes. These results suggest inhibitory inputs could mediate the emergence of grid cell firing in a neuronal network.
Keywords: entorhinal cortex; hyperpolarization-activated cation current (Ih); inhibition; post-inhibitory spikes; stellate cells.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures





References
-
- Alonso A, Klink R. 1993. Differential electroresponsiveness of stellate and pyramidal-like cells of medial entorhinal cortex layer II. J Neurophysiol. 70(1):128–143. - PubMed
-
- Alonso A, Köhler C. 1984. A study of the reciprocal connections between the septum and the entorhinal area using anterograde and retrograde axonal transport methods in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol. 225:327–343. - PubMed
-
- Alonso A, Llinás RR. 1989. Subthreshold Na+-dependent theta-like rhythmicity in stellate cells of entorhinal cortex layer II. Nature. 342(6246):175–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

