Study protocol for a single-blind, placebo-controlled randomised trial of Tianjiu effects in patients with intradialytic hypotension
- PMID: 26966058
- PMCID: PMC4800128
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-009976
Study protocol for a single-blind, placebo-controlled randomised trial of Tianjiu effects in patients with intradialytic hypotension
Abstract
Introduction: Intradialytic hypotension (IDH) is the most frequent complication of haemodialysis (HD) and may contribute to cardiovascular events and high mortality. The aetiology of IDH is multifactorial; therefore, it remains a challenging problem in the management of patients with HD. Since the application of Tianjiu at specific points can influence haemodynamics, we hypothesise that Tianjiu therapy at the traditionally used meridian points will reduce the severity of hypotension in patients who undergo HD.
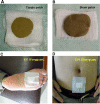
Methods/analysis: In this clinical trial, eligible patients with IDH will be divided randomly and equally into a Tianjiu group and a control group for 4 weeks. In the Tianjiu group, the patients will have Tianjiu applied at three points (conception vessel 4, and bilateral kidney 1) during each HD session. In the control group, patients will have clay patches applied in the same way as those in the Tianjiu treatment group. Both groups will be followed up for 2 weeks. The primary outcome measure will be the percentage of target ultrafiltration achieved, defined as the actual ultrafiltration volume divided by the target ultrafiltration volume. Secondary outcome measures, including frequency of IDH episodes and number of nursing interventions during HD sessions, predialysis and postdialysis blood pressure (BP), patient's participative assessment of the degree of fatigue after dialysis (scale from 0, not at all, to 10, extremely), and recovery time from fatigue after dialysis will be recorded at the 0th and 4th weeks.
Ethics/dissemination: This trial has undergone ethical scrutiny and been approved by the ethics review board of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (Permission number: 102-4749A3 and 104-3156C). The pre-results of this trial will help to determine whether Tianjiu is an effective and safe treatment for IDH, and, if so, whether it is a therapeutic effect rather than a placebo effect.
Trial registration number: NCT02210377; Pre-results.
Keywords: COMPLEMENTARY MEDICINE.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/
Figures
References
-
- Sherman RA, Daugirdas JT, Ing TS. Complications during hemodialysis. In: Daugirdas JT, Blake PG, Ing TS, eds. Handbook of dialysis. 4th edn Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2011:170–91.
-
- K/DOQI Workgroup. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 2005;45(Supplement 3):1–153. - PubMed
-
- Schreiber MJ., Jr Setting the stage. Am J Kidney Dis 2001;38(Supplement 4):1–10. - PubMed
-
- Hekmat R, Ahmadi M, Fatehi H et al. . Correlation between asymptomatic intradialytic hypotension and regional left ventricular dysfunction in hemodialysis patients. Iran J Kidney Dis 2011;5:97–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
