Autism-associated SHANK3 haploinsufficiency causes Ih channelopathy in human neurons
- PMID: 26966193
- PMCID: PMC4901875
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aaf2669
Autism-associated SHANK3 haploinsufficiency causes Ih channelopathy in human neurons
Abstract
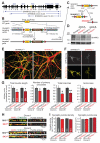
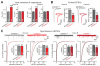
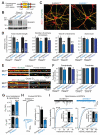
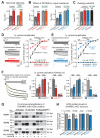
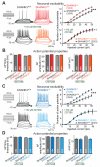
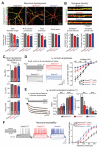
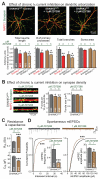
Heterozygous SHANK3 mutations are associated with idiopathic autism and Phelan-McDermid syndrome. SHANK3 is a ubiquitously expressed scaffolding protein that is enriched in postsynaptic excitatory synapses. Here, we used engineered conditional mutations in human neurons and found that heterozygous and homozygous SHANK3 mutations severely and specifically impaired hyperpolarization-activated cation (Ih) channels. SHANK3 mutations caused alterations in neuronal morphology and synaptic connectivity; chronic pharmacological blockage of Ih channels reproduced these phenotypes, suggesting that they may be secondary to Ih-channel impairment. Moreover, mouse Shank3-deficient neurons also exhibited severe decreases in Ih currents. SHANK3 protein interacted with hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel proteins (HCN proteins) that form Ih channels, indicating that SHANK3 functions to organize HCN channels. Our data suggest that SHANK3 mutations predispose to autism, at least partially, by inducing an Ih channelopathy that may be amenable to pharmacological intervention.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures
References
-
- Rosti RO, Sadek AA, Vaux KK, Gleeson JG. The genetic landscape of autism spectrum disorders. Dev. Med. Child Neurology. 2014;56:12–18. - PubMed
-
- Grabrucker AM, Schmeisser MJ, Schoen M, Boeckers TM. Postsynaptic ProSAP/Shank scaffolds in the cross-hair of synaptopathies. Trends Cell Biol. 2011;21:594–603. - PubMed
-
- Carbonetto S. A blueprint for research on Shankopathies: a view from research on autism spectrum disorder. Dev. Neurobiol. 2014;74:85–112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

