A Gain-Of-Function Mutation in the Plcg2 Gene Protects Mice from Helicobacter felis-Induced Gastric MALT Lymphoma
- PMID: 26966907
- PMCID: PMC4788355
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150411
A Gain-Of-Function Mutation in the Plcg2 Gene Protects Mice from Helicobacter felis-Induced Gastric MALT Lymphoma
Abstract
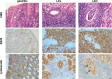
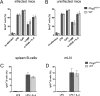
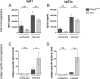
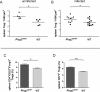
Gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphomas develop from a chronic Helicobacter infection. Phospholipase C gamma 2 (PLCG2) is important for B-cell survival and proliferation. We used BALB/c mice with a gain-of-function mutation in the Plcg2 gene (Ali5) to analyze its role in the development of gastric MALT lymphoma. Heterozygous BALB/c Plcg2Ali5/+ and wildtype (WT) mice were infected with Helicobacter felis (H. felis) and observed up to 16 months for development of gastric MALT lymphomas. In contrast to our initial hypothesis, Plcg2Ali5/+ mice developed MALT lymphomas less frequently than their WT littermates after long-term infection of 16 months. Infected Plcg2Ali5/+ mice showed downregulation of proinflammatory cytokines and decreased H. felis-specific IgG1 and IgG2a antibody responses. These results suggested a blunted immune response of Plcg2Ali5/+ mice towards H. felis infection. Intriguingly, Plcg2Ali5/+ mice harboured higher numbers of CD73 expressing regulatory T cells (Tregs), possibly responsible for impaired immune response towards Helicobacter infection. We suggest that Plcg2Ali5/+ mice may be protected from developing gastric MALT lymphomas as a result of elevated Treg numbers, reduced response to H. felis and decrease of proinflammatory cytokines.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Wotherspoon AC, Ortiz-Hidalgo C, Falzon MR, Isaacson PG. Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis and primary B-cell gastric lymphoma. Lancet. 1991;338(8776):1175–6. Epub 1991/11/09. . - PubMed
-
- Stolte M. Helicobacter pylori gastritis and gastric MALT-lymphoma. Lancet. 1992;339(8795):745–6. Epub 1992/03/21. . - PubMed
-
- Wündisch T, Dieckhoff P, Greene B, Thiede C, Wilhelm C, Stolte M, et al. Second cancers and residual disease in patients treated for gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma by Helicobacter pylori eradication and followed for 10 years. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(4):936–42. Epub 2012/07/04. 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.035 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bayerdörffer E, Neubauer A, Rudolph B, Thiede C, Lehn N, Eidt S, et al. Regression of primary gastric lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue type after cure of Helicobacter pylori infection. MALT Lymphoma Study Group. Lancet. 1995;345(8965):1591–4. Epub 1995/06/24. . - PubMed
-
- Wündisch T, Thiede C, Morgner A, Dempfle A, Günther A, Liu H, et al. Long-term follow-up of gastric MALT lymphoma after Helicobacter pylori eradication. Journal of clinical oncology: official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2005;23(31):8018–24. Epub 2005/10/06. 10.1200/JCO.2005.02.3903 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

