MicroRNAs mediated regulation of MAPK signaling pathways in chronic myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 26967056
- PMCID: PMC5173166
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7977
MicroRNAs mediated regulation of MAPK signaling pathways in chronic myeloid leukemia
Abstract
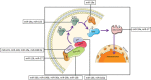
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a severe problem throughout the world and requires identification of novel targets for its treatment. This multifactorial disease accounts for about 15% of the all diagnosed leukemia cases. Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway is crucial for the cell survival and its dysregulation is being implicated in various types of cancers. In here, we have discussed the potential role of various miRNAs that are found involved in regulating the proteins cascades of MAPK signaling pathway associated with CML. An emphasis has been paid to summarize the influence of various miRNAs in elevating or suppressing the expression level of significant proteins such as miR-203, miR-196a, miR-196b, miR-30a, miR-29b, miR-138 in BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase; miR-126, miR-221, miR-128, miR-15a, miR-188-5p, miR-17 in CRK family proteins; miR-155, miR-181a with SOS proteins; miR-155, miR-19a, with KRAS proteins; miR-19a with RAF1 protein; and miR-17, miR-19a, miR-17-92 cluster with MAPK/ERK proteins. In light of ever-increasing importance and ever-widening regulatory roles of miRNAs in cells, we have reviewed the recent progress in the field of miRNAs and have tried to suggest them as controlling targets for various protein cascades of MAPK signaling pathway. An understanding of the supervisory mechanism of MAPK by miRNAs might provide novel targets for treating CML.
Keywords: MAPK; chronic myeloid leukemia; microRNA; oncogenic; signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O, Kolch W. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26:3279–3290. - PubMed
-
- Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, Xu B-e, Karandikar M, Berman K, Cobb MH. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions 1. Endocrine reviews. 2001;22:153–183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

