Spatial Navigation in Preclinical Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 26967209
- PMCID: PMC5091813
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-150855
Spatial Navigation in Preclinical Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
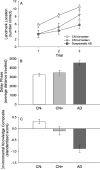
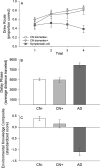
Although several previous studies have demonstrated navigational deficits in early-stage symptomatic Alzheimer's disease (AD), navigational abilities in preclinical AD have not been examined. The present investigation examined the effects of preclinical AD and early-stage symptomatic AD on spatial navigation performance. Performance on tasks of wayfinding and route learning in a virtual reality environment were examined. Comparisons were made across the following three groups: Clinically normal without preclinical AD (n = 42), clinically normal with preclinical AD (n = 13), and early-stage symptomatic AD (n = 16) groups. Preclinical AD was defined based on cerebrospinal fluid Aβ42 levels below 500 pg/ml. Preclinical AD was associated with deficits in the use of a wayfinding strategy, but not a route learning strategy. Moreover, post-hoc analyses indicated that wayfinding performance had moderate sensitivity and specificity. Results also confirmed early-stage symptomatic AD-related deficits in the use of both wayfinding and route learning strategies. The results of this study suggest that aspects of spatial navigation may be particularly sensitive at detecting the earliest cognitive deficits of AD.
Keywords: Aging; allocentric; amyloid; caudate nucleus; egocentric; hippocampus.
Figures
References
-
- Henderson VW, Mack W, Williams BW. Spatial disorientation in Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1989;46:391–394. - PubMed
-
- Pai MC, Jacobs WJ. Topographical disorientation in community-residing patients with Alzheimer's disease. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2004;19:250–255. - PubMed
-
- Tu MC, Pai MC. Getting lost for the first time in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Int Psychogeriatr. 2006;18:567–570. - PubMed
-
- Dubinsky RM, Stein AC, Lyons K. Practice parameter: Risk of driving and Alzheimer's disease (an evidence-based review): Report of the quality standards subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 2000;54:2205–2211. - PubMed
-
- Hunt LA, Brown AE, Gilman IP. Drivers with dementia and outcomes of becoming lost while driving. Am J Occup Ther. 2010;64:225–232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

