Information Integration and Communication in Plant Growth Regulation
- PMID: 26967291
- PMCID: PMC5126258
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.01.044
Information Integration and Communication in Plant Growth Regulation
Abstract
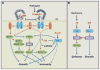
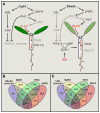
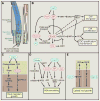
Plants are equipped with the capacity to respond to a large number of diverse signals, both internal ones and those emanating from the environment, that are critical to their survival and adaption as sessile organisms. These signals need to be integrated through highly structured intracellular networks to ensure coherent cellular responses, and in addition, spatiotemporal actions of hormones and peptides both orchestrate local cell differentiation and coordinate growth and physiology over long distances. Further, signal interactions and signaling outputs vary significantly with developmental context. This review discusses our current understanding of the integrated intracellular and intercellular signaling networks that control plant growth.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Achard P, Cheng H, De Grauwe L, Decat J, Schoutteten H, Moritz T, Van Der Straeten D, Peng J, Harberd NP. Integration of plant responses to environmentally activated phytohormonal signals. Science. 2006;311:91–94. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht C, Boutrot F, Segonzac C, Schwessinger B, Gimenez-Ibanez S, Chinchilla D, Rathjen JP, de Vries SC, Zipfel C. Brassinosteroids inhibit pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered immune signaling independent of the receptor kinase BAK1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:303–308. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Babst BA, Ferrieri RA, Gray DW, Lerdau M, Schlyer DJ, Schueller M, Thorpe MR, Orians CM. Jasmonic acid induces rapid changes in carbon transport and partitioning in Populus. New Phytol. 2005;167:63–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

